110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

装载姜黄素的半乳糖基化 BSA 纳米颗粒作为靶向药物递送载体抑制肝细胞癌细胞增殖和迁移
Authors Huang Y, Hu L, Huang S, Xu W, Wan J, Wang D, Zheng G, Xia Z
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 6 November 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 8309—8323
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S184379
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
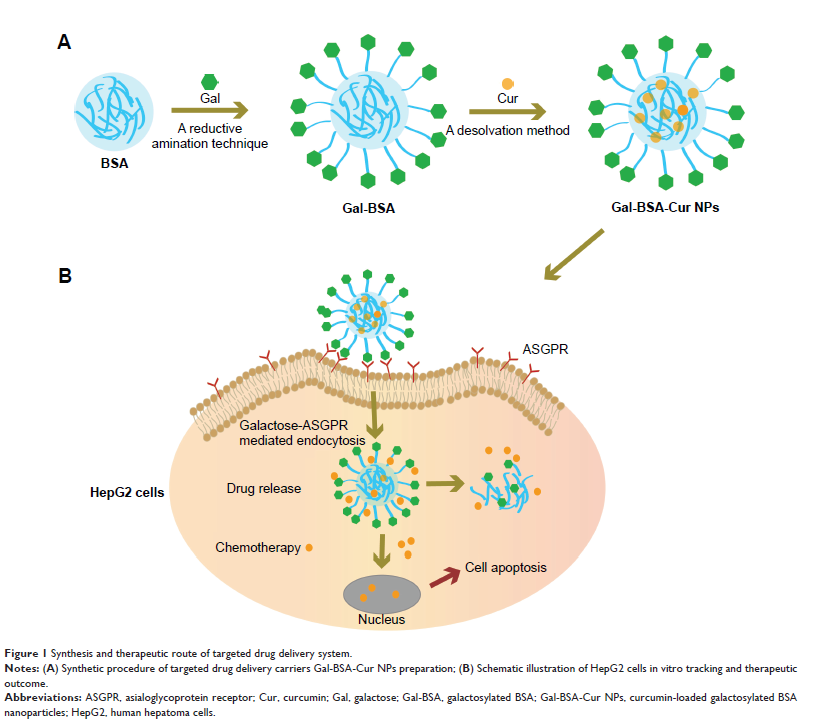
Background: The main
objective of this study was to develop novel BSA nanoparticles (BSA NPs) for
improving the bioavailability of curcumin as an anticancer drug, and those BSA
NPs were galactosylated for forming the curcumin-loaded galactosylated BSA
nanoparticles (Gal-BSA-Cur NPs), thus enhancing their ability to target
asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) overexpressed on hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) cells.
Materials and methods: Gal-BSA-Cur
NPs were prepared by the desolvation method and showed a spherical shape and
well distribution with the average particle size of 116.24 nm.
Results: In vitro
drug release assay exhibited that Gal-BSA-Cur NPs had higher release rates and
improved the curcumin solubility. Cell uptake studies confirmed that
Gal-BSA-Cur NPs could selectively recognize receptors on the surface of HCC
(HepG2) cells and improve internalization ability of drug compared with BSA
NPs-loaded curcumin (BSA-Cur NPs), which might be due to high affinity to
galactose. Further, the effects of Gal-BSA-Cur NPs were evaluated by
cytotoxicity assay, crystal violet assay, cell apoptosis assay, and wound
healing assay, respectively, which revealed that Gal-BSA-Cur NPs could inhibit
HepG2 cells proliferation, induce cell apoptosis, and inhibit cell migration.
Conclusion: Immunofluorescence
staining has proved that the effects of Gal-BSA-Cur NPs related to the
suppression of the nuclear factor κB-p65 (NF-κB-p65) expression in HepG2 cell
nucleus. Therefore, these results indicate that novel Gal-BSA-Cur NPs are
potential candidates for targeted curcumin delivery to HCC cells.
Keywords: albumin,
curcumin, nanoparticles, galactosylated, hepatocellular carcinoma