110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

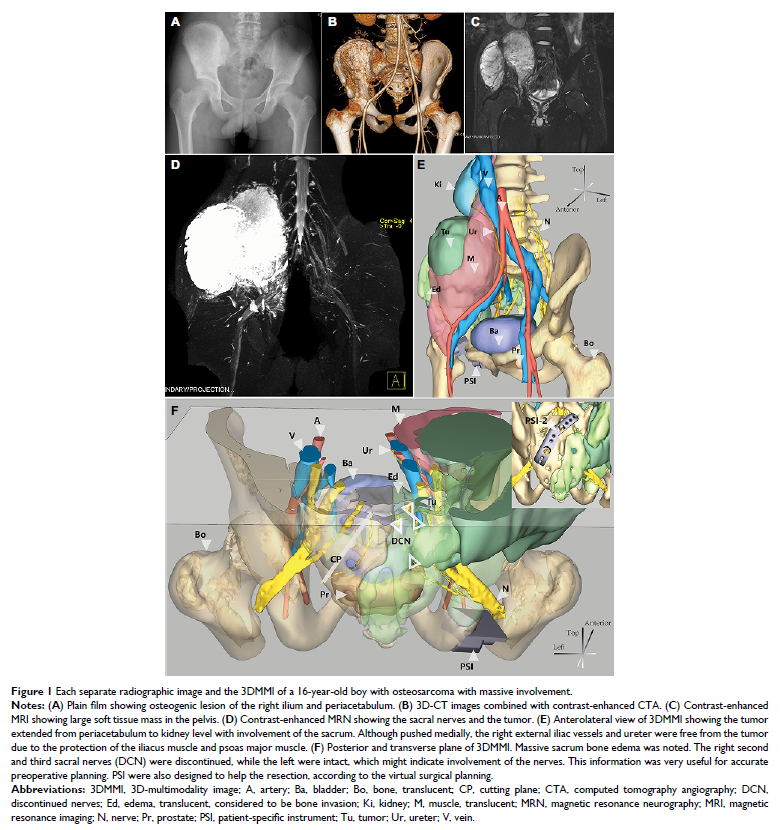
拥有三维多模态图像、经改进的虚拟手术计划用于恶性巨骨盆肿瘤治疗
Authors Fang X, Yu Z, Xiong Y, Yuan F, Liu H, Wu F, Zhang W, Luo Y, Song L, Tu C, Duan H
Received 29 August 2018
Accepted for publication 28 October 2018
Published 7 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6769—6777
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185737
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Purpose: We sought
to assess the early clinical outcome of 3D-multimodality image (3DMMI)-based
virtual surgical planning for resection and reconstruction of malignant giant
pelvic tumors.
Patients and methods: In this
retrospective case-control study, surgery was planned and performed with
3DMMI-based patient-specific instruments (PSI) in 13 patients with giant pelvic
malignancy and without 3DMMI-based PSI in the other 13 patients. In the 3DMMI
group, 3DMMI was utilized, taking advantages of computed tomography (CT),
contrast-enhanced CT angiography (CTA), contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI), contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance neurography (MRN), which
could reveal the whole tumor and all adjacent vital structures. Based on these
3DMMI, virtual surgical planning was conducted and the corresponding PSI was
then designed. The median follow-up was 8 (3–24) months. The median age at
operation was 37.5 (17–64) years. The mean tumor size in maximum diameter was
13.3 cm. Surgical margins, intraoperative and postoperative complications,
duration of surgery, and intra-operative blood loss were analyzed.
Results: In the
non-3DMMI group, the margins were wide in six patients (6/13), marginal in four
(4/13), wide-contaminated in two (2/13), and intralesional in one (1/13). In
the 3DMMI group, the margins were wide in 10 patients (10/13), marginal in
three (3/13), and there were no wide-contaminated or intralesional margins. The
3DMMI group achieved shorter duration of surgery (P =0.354) and lower
intraoperative blood loss (P =0.044) than the non-3DMMI group.
Conclusion: The
3DMMI-based technique is advantageous to obtain negative surgical margin and
decrease surgical complications related to critical structures injury for
malignant giant pelvic tumor.
Keywords: surgical
planning, 3D-multimodality image, pelvic tumor, patient-specific instruments,
surgical margin