110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Delta-6 去饱和酶抑制剂在体外和体内增强胶质母细胞瘤的放射治疗
Authors Wang J, Liang H, Sun M, Zhang L, Xu H, Liu W, Li Y, Zhou Y, Li Y, Li M
Received 28 August 2018
Accepted for publication 4 November 2018
Published 7 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6779—6790
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185601
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: It has
been reported that cell inflammation pathways contribute to the development of
prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-inhibitor of DNA-binding protein-1 (ID1)-dependent
radioresistance in glioblastoma. Here, we proposed that inhibiting
delta-6-desaturase (D6D) could block arachidonic acid synthesis and PGE2
production, thereby reversing PGE2-ID1-dependent radioresistance in
glioblastoma cells and xenograft tumor models.
Materials and methods: Two
glioblastoma cell lines, namely, U-87 MG and LN-229, were used for the in vitro
study. The combination effects of SC-26196 (a D6D inhibitor) and radiation were
assessed by the MTS assay, colony formation assay, and cell apoptosis analysis.
HPLC/MS analysis was performed to quantify the production of arachidonic acid
and PGE2. For the in vivo study, 6-week-old nude mice, each bearing a U-87 MG
xenograft tumor, were subjected to 4-week treatments of vehicle, SC-26196,
radiation, or the combination of both. Tumor growth was monitored during the
treatment, and the tumor tissues were collected at the end for further
analysis.
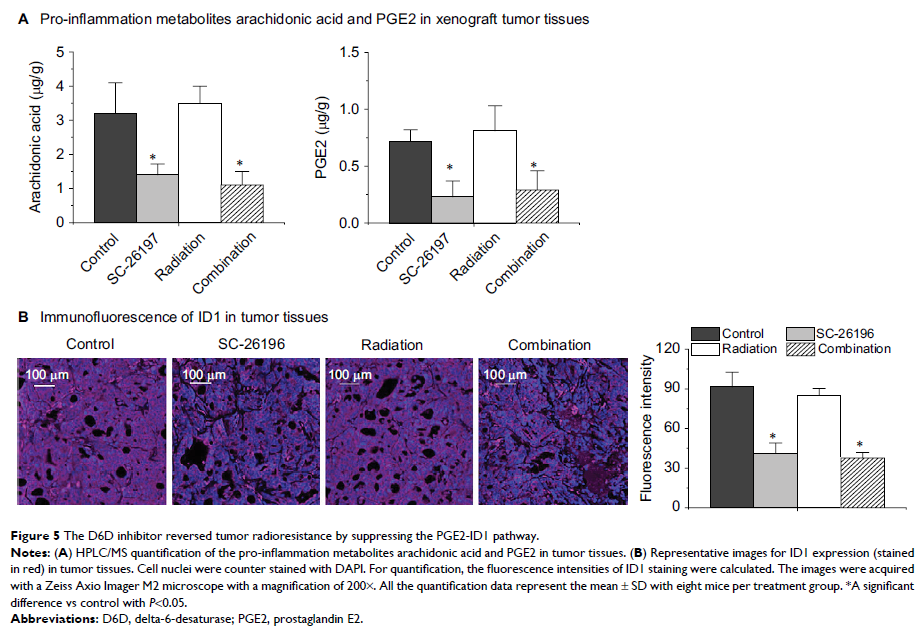
Results: Treatment
with SC-26196 significantly improved radiosensitivity in both glioblastoma cell
lines in vitro, and radiosensitivity was associated with inhibited synthesis of
arachidonic acid and PGE2. The combination of SC-26196 and radiation
synergistically inhibited U-87 MG xenograft tumor growth, in association with
the induction of tumor apoptosis and suppressed tumor proliferation. SC-26196
also inhibited arachidonic acid and PGE2 production in vivo and limited
expression of ID1.
Conclusion: These data
suggested that the D6D inhibitor could reverse PGE2-ID1-dependent
radioresistance in glioblastoma cells and xenograft tumor models by blocking
the synthesis of arachidonic acid and PGE2. Although further investigation is
required, the outcomes from this study may guide us in developing a potentially
novel combination strategy for current glioblastoma therapy.
Keywords: delta-6-desaturase,
glioblastoma, radiation therapy, inflammation pathway