110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

万古霉素治疗成人腹腔感染: 我们是否有强有力的证据?
Authors Liu S, Wang M, Guan W
Received 25 August 2018
Accepted for publication 16 November 2018
Published 7 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2539—2543
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S185331
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Abstract: The management
of intra-abdominal infections (IAIs) primarily includes adequate antimicrobial
therapy and appropriate source control. Vancomycin is a fundamental and most
effective antimicrobial agent. The aim of this study is to search and evaluate
the quality of clinical evidences regarding the exclusive use of vancomycin for
the management of adult IAIs. For this purpose, we first summarized the
recommendations on exclusive use of vancomycin in adult IAIs from six leading
guidelines and excavated the relevant supporting references. We subsequently
conducted a literature search to screen eligible clinical studies in this field
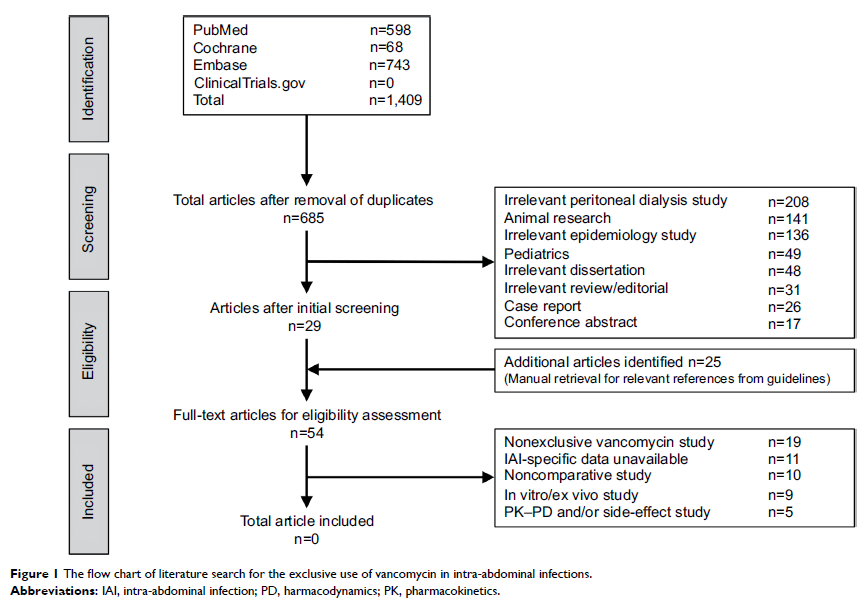
for possible systematic review. Our investigation demonstrates that the
exclusive use of vancomycin is recommended in restricted indications, that is,
IAIs caused by Enterococcus spp . or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus .
However, the supporting references in the guidelines are more subjective
instead of objective, which mainly originate from experts’ personal experiences
or from the therapeutic efficacy of vancomycin in other types of infections
rather than in IAIs. Furthermore, our literature search fails to find
high-level evidence. In conclusion, current low-level evidences are inadequate
to elicit strong recommendations on the exclusive use of vancomycin in the
treatment of adult IAIs. Our study would be helpful for the rational use of
vancomycin and deceleration of the emerging vancomycin resistance rates.
Keywords: intra-abdominal
infection, vancomycin, guideline, anti-infective agents