110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA SNHG16 过表达通过功能性海绵 hsa-miR-93 抑制 HCC 增殖和化疗耐药
Authors Xu F, Zha G, Wu Y, Cai W, Ao J
Received 31 July 2018
Accepted for publication 31 August 2018
Published 7 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8855—8863
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182005
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Long noncoding
RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified as prognostic biomarkers and functional
regulators in human cancers. The present study aimed to determine the
expressions and functions of an lncRNA, Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 16 (SNHG16 ), in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Patients and methods: SNHG16 expressions
were tested by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in HCC cell lines, as well
as 43 pairs of HCC tissues and pair-matched healthy hepatic tissues. It was
overexpressed in Hep3B and HuH7 cells. The effects of SNHG16 overexpression
in HCC in vitro proliferation, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) chemoresistance, and
in vivo tumor growth were tested. A potential microRNA (miRNA) sponge
target of SNHG16 ,
hsa-miR-93, was tested by luciferase reporter assay and qRT-PCR. In addition,
hsa-miR-93 was upregulated in SNHG16 -overexpressed HCC cells to examine its effect
on SNHG16 -mediated
cancer cell functional regulation in HCC.
Results: SNHG16 levels
were markedly downregulated in both HCC cell lines and HCC tissues.
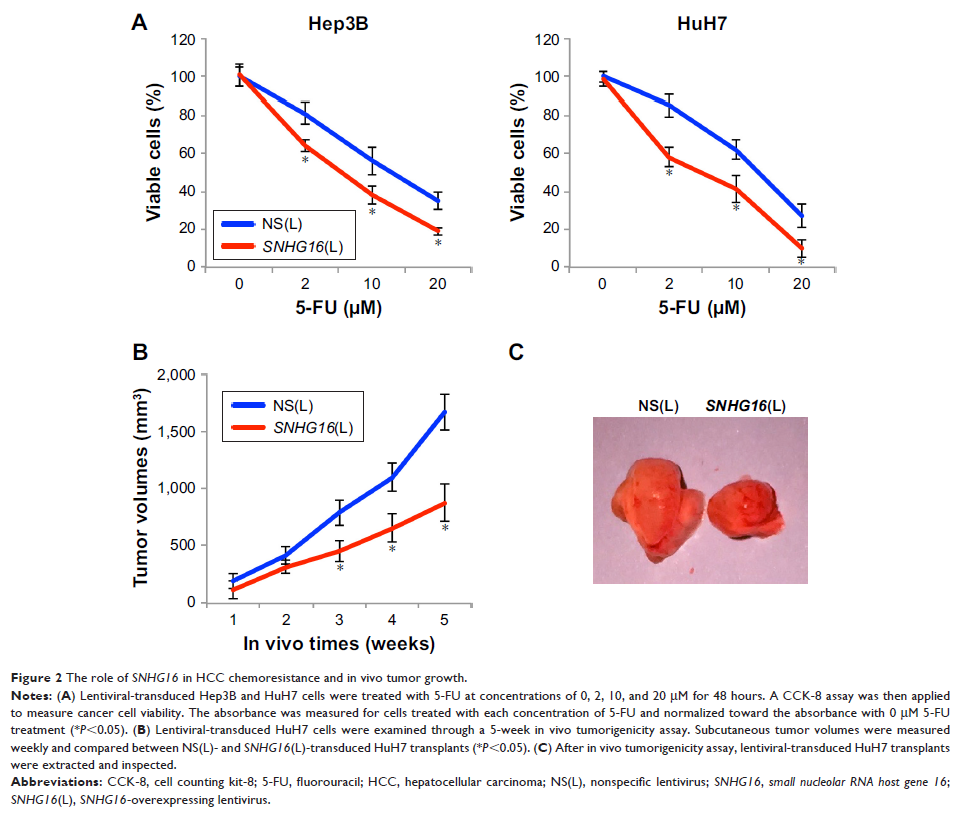
Lentivirus-mediated SNHG16 overexpression inhibited HCC cell proliferation,
5-FU chemoresistance, and in vivo tumor growth. Hsa-miR-93 was confirmed
to be directly sponging on SNHG16 . Its upregulation in HCC cells reversed SNHG16 overexpression
and induced tumor-suppressing effects in HCC cells.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate
that SNHG16 plays
a critical role in HCC development via functionally sponging hsa-miR-93.
Keywords: lncRNA, SNHG16 , miRNA,
hsa-miR-93, proliferation