110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

年龄和复发性卒中与有糖尿病的腔隙性脑梗死患者的白质高信号严重程度有关
Authors Yu L, Yang L, Zhang X, Yuan J, Li Y, Yang S, Gu H, Hu W, Gao S
Received 18 August 2018
Accepted for publication 1 November 2018
Published 7 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2487—2494
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S184463
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background and purpose: White
matter hyperintensities (WMH) is identified as a marker of cerebral small
vessel diseases and is a major contributor to cognitive impairment, depression,
gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence. However, the risk factors for WMH
in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has not been well explored. Thus,
in this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between the severity of
WMH and vascular risk factors in lacunar infarction patients with T2DM.
Methods: Consecutive
lacunar infarction patients with T2DM were recruited in this cross-sectional study.
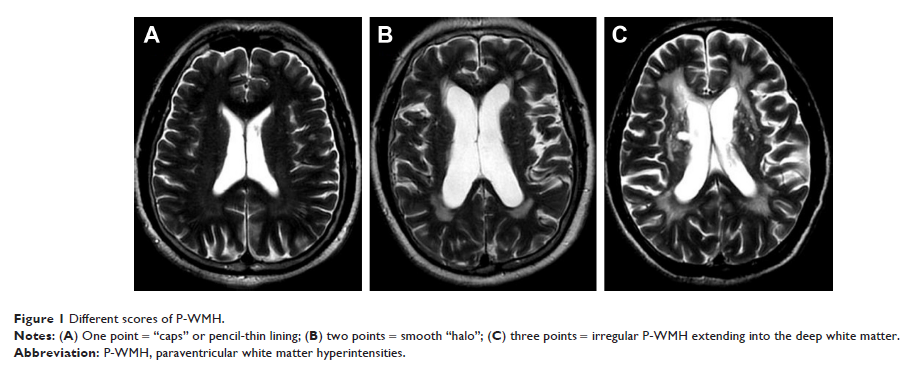
Paraventricular WMH (P-WMH) and deep WMH (D-WMH) were separately scored by the
Fazekas scale, and classified into two categories by the severity. Vascular
risk factors and clinical features were compared between the mild and severe
WMH. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to determine the
relationship between severity of WMH and vascular risk factors.
Results: A total
of 327 participants aged 34–91 years were enrolled in this study. Compared with
the patients with mild P-WMH, the patients with severe P-WMH had higher age (P =0.031), higher
proportion of hypertension (P =0.042) and stroke (P <0.001). Levels
of TG, LDL, and HbA1c were significantly higher in patients with mild P-WMH.
Compared with the patients with mild D-WMH the patients with severe D-WMH had
higher age and hyperhomocysteinemia (HCY) level (P <0.001), higher
proportion of hyperlipidemia (P =0.008), and stroke (P <0.001).
Multivariable logistic regression analyses showed that higher age and recurrent
stroke were independently related to severe P-WMH and D-WMH in lacunar
infarction patients with T2DM.
Conclusions: Age and
recurrent stroke are related to the severity of P-WMH and D-WMH in lacunar
infarction patients with T2DM.
Keywords: lacunar
infarction, type 2 diabetes mellitus, white matter hyperintensities,
leukoaraiosis