110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ADAR1 沉默诱导的 HUVEC 凋亡是在缺氧胁迫下由 FGFR2 介导的
Authors Jiang Y, Wang Z, Chen X, Wang W, Wang X
Received 24 July 2018
Accepted for publication 1 October 2018
Published 10 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4181—4189
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S181312
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Background: The
adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 (ADAR1) specifically deaminates adenosine
to inosine in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Emerging evidence indicated that
under hypoxia condition, such as tumor microenvironment, ADAR1 level was
increased. Interestingly, we found FGFR2 was also increased under hypoxia
stress. The purpose of this study was to investigate the regulation mechanism
of ADAR1 and the potential role of ADAR1–FGFR2 axis in cell proliferation and
apoptosis.
Methods: Using
human umbilical vein endothelial cells as cellular model, we explored the
function of ADAR1 in regulating cell survival.
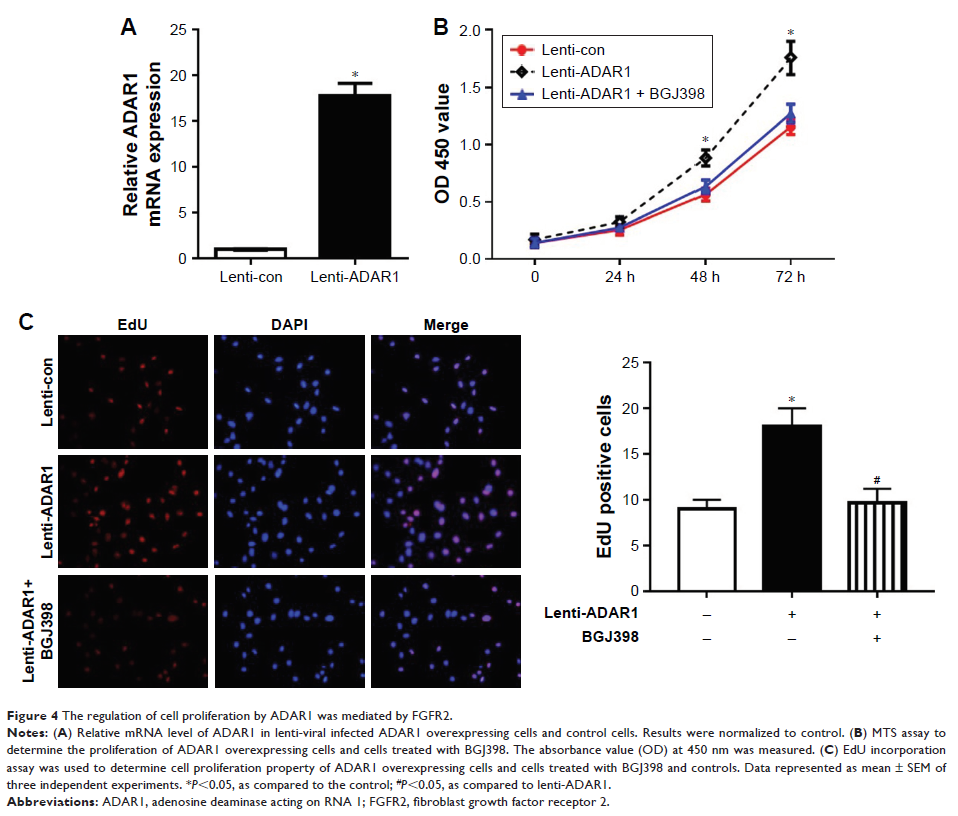
Results: We found
manipulation of FGFR2 activity could override the cellular effect of ADAR1,
suggesting FGFR2 could be a potential effector of ADAR1. Moreover, our results
revealed that PI3K-Akt pathway was involved in ADAR1–FGFR2 axis-induced cell
proliferation.
Conclusion: In
summary, this study supported the notion that ADAR1 could play a role in tumor
cell proliferation, which was mediated by FGFR2.
Keywords: ADAR1,
HUVEC, FGFR2, apoptosis, hypoxia, PI3K-Akt pathway