110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ILF3 和 lncRNA ILF3-AS1 之间的正反馈环路可促进黑素瘤增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Gao G, Li W, Liu S, Han D, Yao X, Jin J, Han D, Sun W, Chen X
Received 7 September 2018
Accepted for publication 11 October 2018
Published 11 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6791—6802
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S186777
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Purpose: In our
previous study, we identified that lncRNA ILF3 antisense RNA 1 (ILF3-AS1) is
increased and has oncogenic roles in melanoma. However, the cause of the
upregulation of ILF3-AS1 and the modulation between ILF3-AS1 and ILF3 in melanoma
are still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the significances of the
interaction between ILF3-AS1 and ILF3 in melanoma.
Materials and methods: The
expression of ILF3 in melanoma tissues and cell lines was measured by
quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The interactions between ILF3-AS1 and
ILF3 were explored by the RNA immunoprecipitation assay, the transcription
inhibition assay, qRT-PCR, the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, and Western
blot. Gain-of-function and loss-of-function assays were performed to
investigate the effects of ILF3 and ILF3-AS1 on melanoma proliferation,
migration, and invasion.
Results: ILF3 is also
increased in melanoma tissues and cell lines. Increased expression of ILF3
predicts poor survival of melanoma patients. Mechanistic investigation revealed
that ILF3 directly binds ILF3-AS1, increases ILF3-AS1 transcript stability, and
upregulates ILF3-AS1 transcript levels. ILF3-AS1 represses the binding of EZH2
to the promoter of ILF3 , induces euchromatin formation at ILF3 promoter,
and activates ILF3 transcription. Thus, ILF3 and ILF3-AS1 form
positive feedback loop, which induces the upregulation of ILF3 and ILF3-AS1 in
melanoma. The expression of ILF3-AS1 is positively correlated with ILF3 in
melanoma tissues. Functional assays revealed that overexpression of ILF3
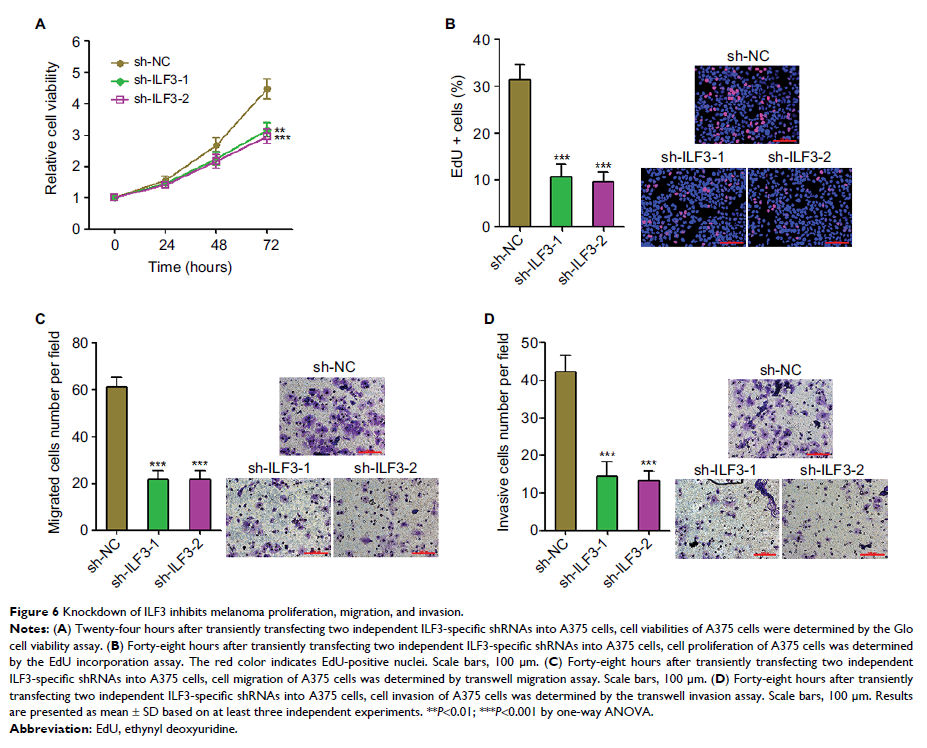
promotes melanoma proliferation, migration, and invasion. Depletion of ILF3
inhibits melanoma proliferation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, concurrent
depletion of ILF3 and ILF3-AS1 significantly suppresses melanoma proliferation,
migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: Both ILF3-AS1
and ILF3 are increased in melanoma. ILF3-AS1 and ILF3 positively regulate each
other. Concurrent targeting ILF3-AS1 and ILF3 has significant tumor-suppressive
roles in melanoma. Our data suggested that targeting the positive feedback loop
between ILF3 and ILF3-AS1 may be promising therapeutic strategies for melanoma.
Keywords: lncRNA,
ILF3-AS1, feedback loop, ILF3, melanoma, progression