110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雷公藤红素诱导乳腺癌细胞中 mTOR 的泛素依赖性降低
Authors Li X, Zhu G, Yao X, Wang N, Hu R, Kong Q, Zhou D, Long L, Cai J, Zhou W
Received 12 September 2018
Accepted for publication 24 October 2018
Published 11 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8977—8985
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187315
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
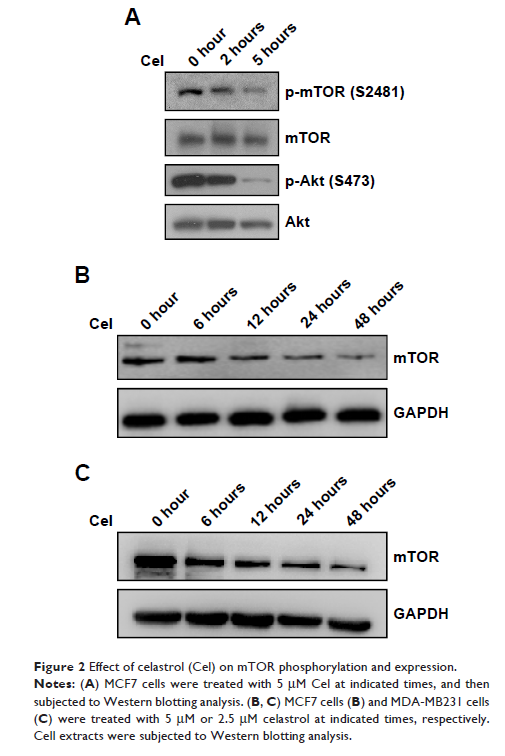
Background: Celastrol
is a major active component of the thunder god vine (Tripterygium wilfordii )
used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat chronic inflammatory and
autoimmune diseases. Celastrol inhibits PI3K–Akt–mTOR signaling, which is
frequently dysregulated in tumors and critical for tumor-cell proliferation and
survival, but the underlying mechanisms are still not fully understood. In the
present study, we investigated detailed mechanisms of celastrol inhibition of
mTOR signaling in breast cancer cells.
Methods: First, we
evaluated the effect of celastrol on breast cancer-cell growth using MTT
assays. Second, we examined the effects of celastrol on mTOR phosphorylation
and expression using Western blot. Furthermore, we investigated the cause of
mTOR downregulation by celastrol using immunoprecipitation assays. In addition,
we evaluated the effect of celastrol on an MDA-MB231 cell-derived xenograft
model.
Results: Celastrol
suppressed breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Celastrol inhibited
mTOR phosphorylation and induced mTOR ubiquitination, resulting in its
proteasomal degradation. Mechanistically, we found that mTOR is a client of
Hsp90–Cdc37 chaperone complex, and celastrol disrupts mTOR interaction with
chaperone Hsp90 while promoting mTOR association with cochaperone Cdc37.
Conclusion: Our study
reveals that celastrol suppresses mTOR signaling, at least in part through
regulating its association with chaperones and inducing its ubiquitination.
Keywords: celastrol,
mTOR, Hsp90, Cdc37, ubiquitin, Chinese medicine