110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

新型 STAT3 抑制剂 HJC0152 在胃癌中具有良好的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Jiang X, Wu M, Xu Z, Wang H, Wang H, Yu X, Li Z, Teng L
Received 21 September 2018
Accepted for publication 15 November 2018
Published 12 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6857—6867
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188364
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: Aberrant
activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is
frequently seen in patients with gastric cancer (GC), and is generally
associated with worse prognosis. HJC0152, a novel STAT3 inhibitor, has shown
significant anti-tumor effects in several cancers, although its role in GC
remains to be clarified.
Methods: The
effect of HJC0152 on STAT3 signaling pathway and the biological behaviors of GC
cells were evaluated through in vitro and/or in vivo experiments. Meanwhile,
RNA sequence analysis was used to further explore its potential anti-tumor
mechanisms.
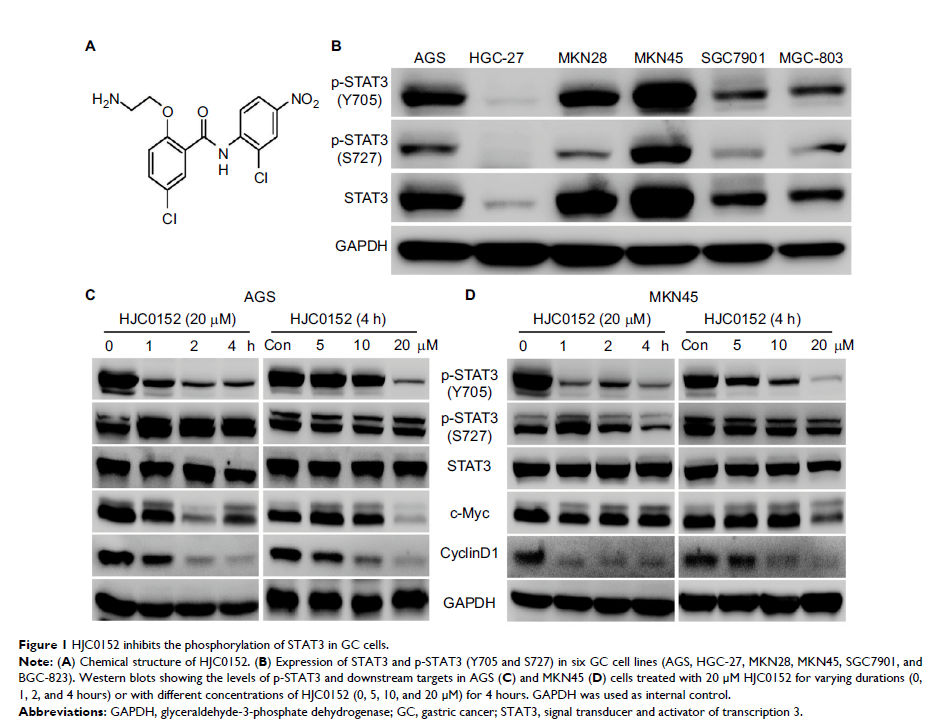
Results: HJC0152
inhibited the expression of activated STAT3 and its downstream target genes
(c-Myc and clyclinD1) in GC cells, and restrained tumor growth in vivo. HJC0152
treatment induced apoptosis in the STAT3 hyper-activated AGS and MKN45 cell
lines, along with down-regulation of survivin and Mcl1, and up-regulation of
cleaved-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Moreover, HJC0152 markedly inhibited
migration and invasion of these cells. Finally, RNA sequence analysis and protein
expression analyses showed that in addition to STAT3 suppression, HJC0152 also
exerts its anti-tumor effects at least partly via the mitogen-activated protein
kinases pathway.
Conclusion: Our
findings highlight that HJC0152 is a promising therapeutic agent for GC.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, inhibitor, HJC0152, STAT3, MAPK