110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-769 在结直肠癌中下调,通过直接靶向周期蛋白依赖性激酶1抑制癌症进展
Authors Wang L, Xu M, Lu P, Zhou F
Received 14 August 2018
Accepted for publication 10 October 2018
Published 12 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 9013—9025
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S183847
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: In recent
years, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to be aberrantly expressed in
colorectal cancer (CRC). The deregulation of miRNAs is implicated in the
formation and progression of CRC, and participates in the regulation of a wide
range of biological behaviors. Considering the crucial role of miRNAs in CRC,
miRNAs are thought to have significant promise in the diagnosis and therapy of
patients with this malignancy.
Material and methods: Reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed to
detect miR-769 expression in CRC tissues and cell lines. MTT assay and flow
cytometry analysis were used to determine the effects of miR-769 upregulation
in CRC cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. The influence of miR-769
overexpression in CRC cell migration and invasion was evaluated through
migration and invasion assays. Notably, the possible mechanisms underlying the
action of miR-769 in CRC cells were explored.
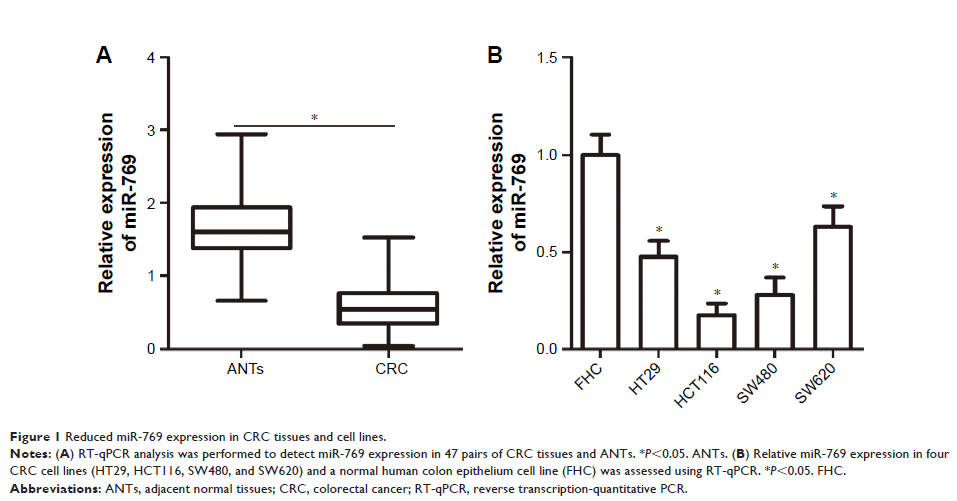
Results: In the
present study, miR-769 was frequently found to be poorly expressed in CRC
tissues and cell lines. Functional assays showed that recovery of miR-769
expression suppressed CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion,
increased cell apoptosis in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) was the direct target of miR-769 in CRC cells.
CDK1 was overexpressed in CRC tissue samples and negatively correlated with
miR-769 expression. In addition, CDK1 inhibition imitated the tumor suppressor
activity of miR-769 in CRC cells, and restoration of CDK1 expression partially
abolished the tumor-suppressing roles of miR-769 in malignant CRC cells.
Conclusion: The
results of this study demonstrated that miR-769 was downregulated in CRC and
directly targeted CDK1 to be implicated in the regulation of CRC cell
proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Thus, the miR-769/CDK1 axis
might be an effective therapeutic target for treating patients with CRC.
Keywords: colorectal
cancer, microRNA-769, proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, cyclin-dependent
kinase 1