110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TSPAN7 通过上皮 - 间质转化促进肺癌细胞的迁移和增殖
Authors Wang X, Lin M, Zhao J, Zhu S, Xu M, Zhou X
Received 12 March 2018
Accepted for publication 8 August 2018
Published 13 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8815—8822
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S167902
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Purpose: To
explore the effects and mechanisms of tetraspanin TSPAN7 on the progression of
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells.
Patients and methods: All 125
lung cancer specimens and 60 metastatic tissues were obtained from patients
diagnosed with NSCLC, and we used immunohistochemistry to detect the expression
of TSPAN7 in NSCLC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. Cell proliferation and
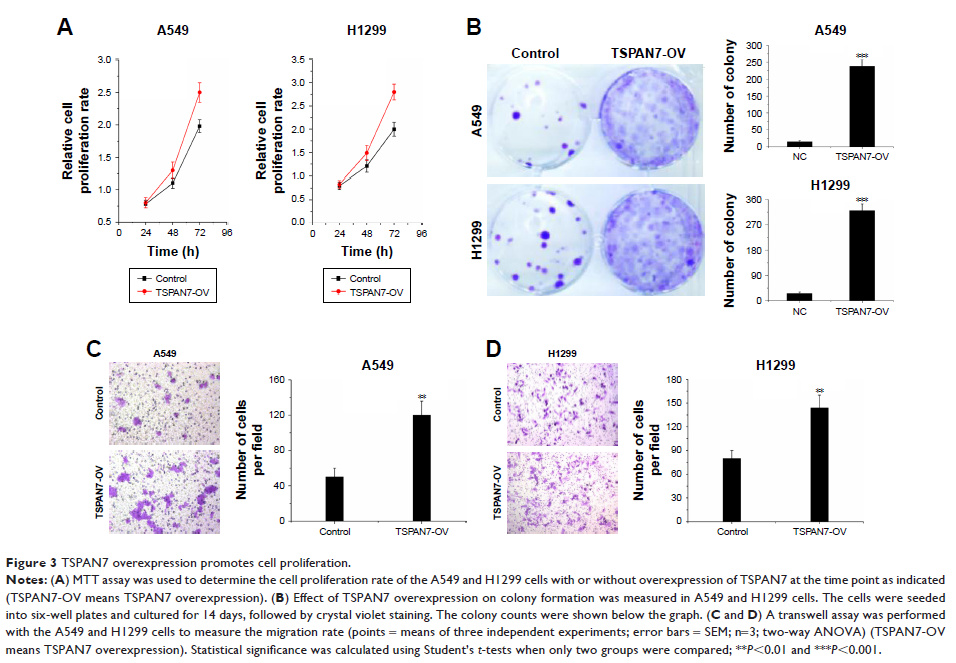
invasion ability were determined by MTT, colony formation, and cell migration.
The relative protein expression level was analyzed by Western blot analysis.
Results: Our
clinical data showed that among 125 patients with lung cancer, TSPAN7 was
associated with lymph node status, differentiation, tumor size, and poor
prognosis. TSPAN7 knockout inhibited cell proliferation and migration. In
addition, TSPAN7 increased the expression of N-cadherin in NSCLC cells by
reducing the expression of E-cadherin and vimentin and promoting the cell
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Xenograft transplantation
model confirmed the role of TSPAN7 in NSCLC metastasis.
Conclusion: TSPAN7-mediated
EMT is the key to NSCLC migration. TSPAN7 is a potential target for NSCLC
therapy.
Keywords: TSPAN7,
non-small-cell lung cancer, cell invasion, colony formation