110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Activation of IL-8 and its participation in cancer in schizophrenia patients: new evidence for the autoimmune hypothesis of schizophrenia
Authors Xu LZ, Qi X, Zhu C, Wan LH
Received 22 September 2018
Accepted for publication 30 November 2018
Published 13 December 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 3393—3403
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S188210
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Abstract: To investigate
the autoimmune mechanisms of schizophrenia, we explored the relationship
between schizophrenia and cancer using gene expression data of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells from GSE27383 datasets. Gene screening and enrichment
analysis using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis were applied to identify possible
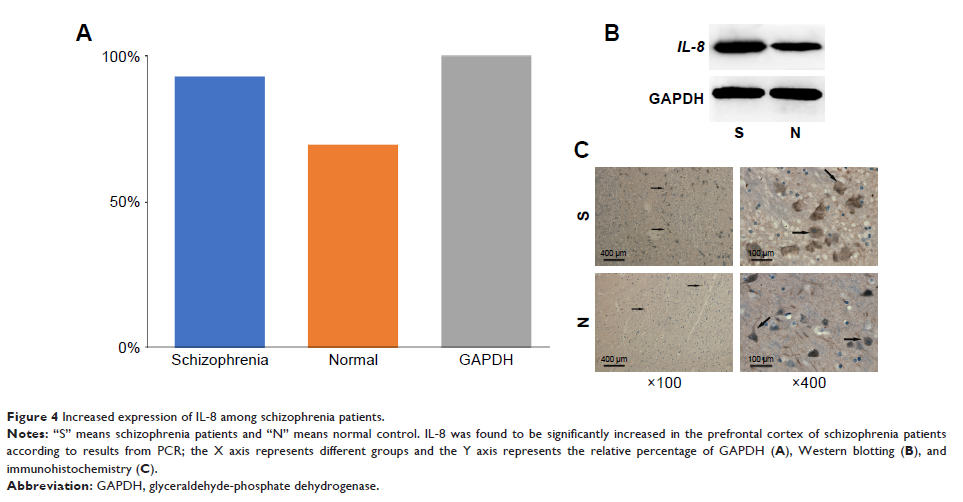
connections between schizophrenia and cancer. Real-time PCR (quantitative PCR),
Western blotting and immunohistochemistry were performed on the brain tissue
from both schizophrenia patients and normal controls. The genes for IL-8 , as well
as PTGS2 , TPR , JUN , CXCL1 , CXCL3 , CXCL5 and PARD3 were
highly expressed in schizophrenia patients. Cancer and chemokine signaling
pathways were enriched in the schizophrenic group, related to the high
expression of IL-8 . Increased expression of IL-8 was further
confirmed by quantitative PCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry
results. Our results suggest that IL-8 may participate specifically in the
pathophysiological changes that occur in schizophrenia. Additionally, our
findings provide novel evidence supporting the autoimmune hypothesis of
schizophrenia.
Keywords: bioinformatics,
multiple primary cancers, autoimmune disease, cancer pathway, GSEA