110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MTDH/AEG-1 在膀胱尿路上皮癌中的临床意义和作用:基于免疫组织化学、RNA-seq 和体外验证的研究
Authors Zhang Y, Zhang LJ, Dang YW, Li SH, Yan HB, Chen G
Received 11 June 2018
Accepted for publication 27 July 2018
Published 14 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6921—6936
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S176887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: Overexpression
of metadherin/astrocyte
elevated gene-1 (MTDH/AEG-1) has been implicated in various
cancers. However, the clinical significance and the potential biological
functions of MTDH/AEG-1 in bladder urothelial carcinoma (BUC) are not
established.
Methods: In this
study, the expression of MTDH/AEG-1in BUC was measured using the Cancer Genome
Atlas (TCGA) database and immunohistochemistry, together with a meta-analysis,
to investigate the expression and diagnostic value of MTDH/AEG-1. The possible
association between MTDH/AEG-1 expression and the viability, proliferation, and
apoptosis in BUC cell lines (T24, HT1376, and RT4) was also assessed in vitro
by viability, MTS, colony formation, and caspase-3/7 assays, as well as Hoechst
33342 and propidium iodide (PI) double staining.
Results: MTDH/AEG-1
expression was significantly higher in BUC tissues than in normal bladder
tissues, according to the TCGA and immunohistochemistry results, and these
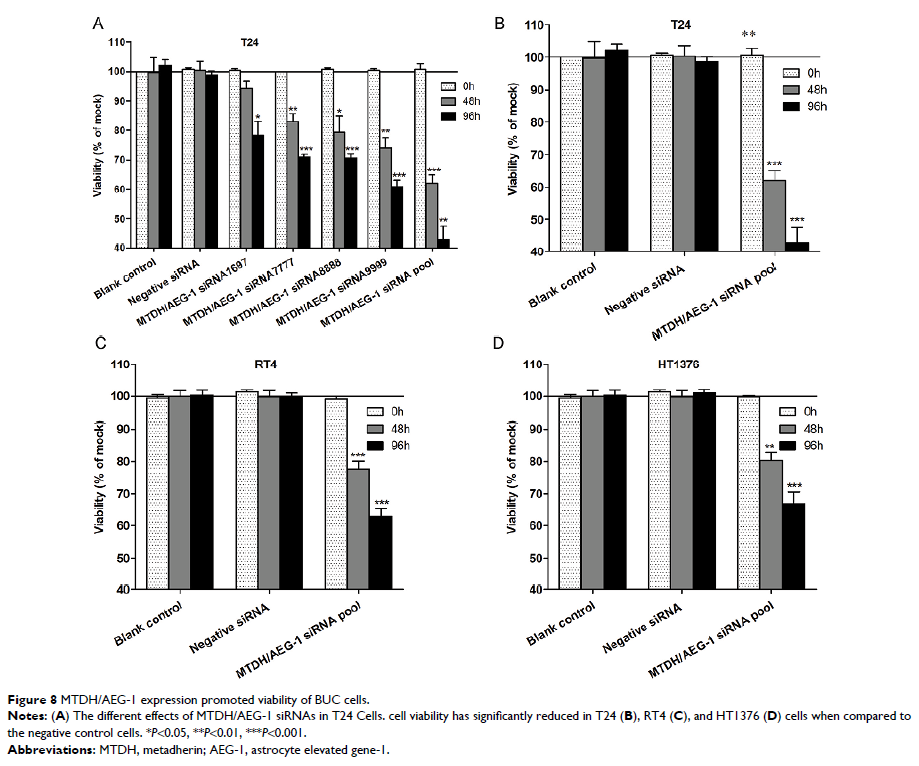
findings were verified by the meta-analysis. Functional knockdown of MTDH/AEG-1
suppressed BUC cell growth and induced apoptosis. Bioinformatics analyses
indicated an involvement of MTDH/AEG-1 in several processes, including RNA
binding, protein transport, intracellular transport, and the insulin signaling
pathway.
Conclusion: We
hypothesize that MTDH/AEG-1 could play essential roles in BUC, especially in
cell growth and apoptosis, via the insulin signaling pathway.”
Keywords: MTDH,
AEG-1, bladder urothelial cancer, meta-analysis