110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

3-正-丁基苯酞在体外缺血性脑卒中模型中通过增强抗氧化和减弱线粒体功能障碍发挥神经保护作用
Authors Chen N, Zhou Z, Li J, Li B, Feng J, He D, Luo Y, Zheng X, Luo J, Zhang J
Received 2 October 2018
Accepted for publication 26 October 2018
Published 14 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4261—4271
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S189472
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: This
study examined whether the neuroprotective drug, 3-n -butylphthalide
(NBP), which is used to treat ischemic stroke, prevents mitochondrial
dysfunction.
Materials and methods: PC12
neuronal cells were pretreated for 24 hours with NBP (10 µmol/L), then exposed
to oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) for 8 hours as an in vitro model
of ischemic stroke. Indices of anti-oxidative response, mitochondrial function
and mitochondrial dynamics were evaluated.
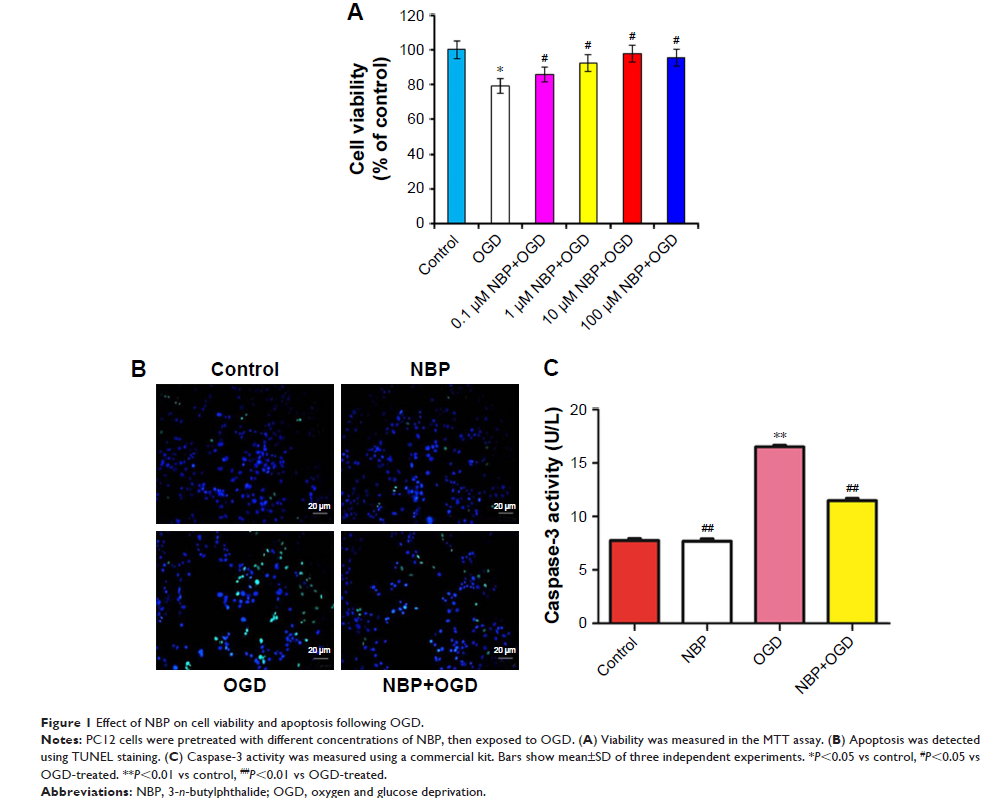
Results: OGD
suppressed cell viability, induced apoptosis and increased caspase-3 activity.
NBP significantly reversed these effects. NBP prevented oxidative damage by
increasing the activity of superoxide dismutase and lowering levels of
malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). At the same time, it
increased expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and AMPK. NBP attenuated mitochondrial
dysfunction by enhancing mitochondrial membrane potential and increasing the
activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I–IV and ATPase. NBP
altered the balance of proteins regulating mitochondrial fusion and division.
Conclusion: NBP
exerts neuroprotective actions by enhancing anti-oxidation and attenuating
mitochondrial dysfunction. Our findings provide insight into how NBP may exert
neuroprotective effects in ischemic stroke and raise the possibility that it
may function similarly against other neurodegenerative diseases involving
mitochondrial dysfunction.
Keywords: ischemic
stroke, mitochondrial dysfunction, mitochondrial dynamics, neuroprotective