110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

出院后延长护理有助于 COPD 患者的疾病控制:一项中国病例研究
Authors Li M, Hu R, Liu X, Tao S, Rong B
Received 12 June 2018
Accepted for publication 6 October 2018
Published 14 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4005—4013
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S177038
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Chunxue Bai
Background: The aim of this
study was to evaluate the efficacy of extended care in patients with COPD.
Patients and methods: A total
of 140 patients with GOLD-2 to -4 of COPD were included in final analysis. The
care efficacy was evaluated by the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
12-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12), pulmonary function test and
blood gas analysis.
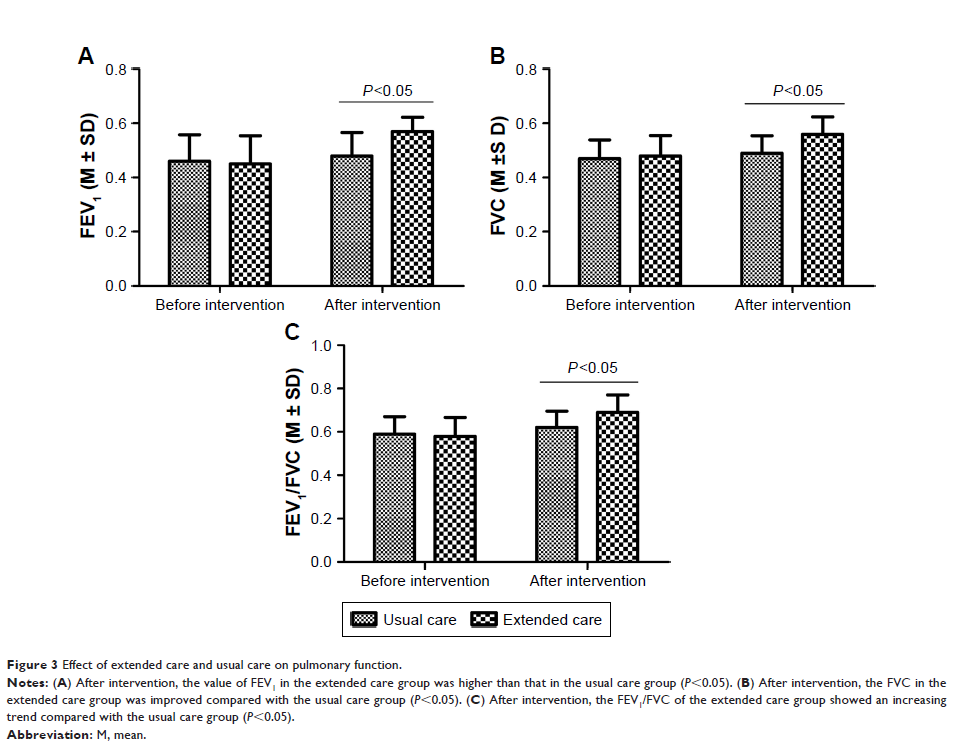
Results: The
extended care improved the activity ability of COPD patients, relieved the
clinical symptoms as well as reduced the impact degree of COPD to daily life (P <0.05). In
addition, the extended care improved the mental health condition of patients
with COPD compared with usual care (P <0.05). Moreover, the extended care improved the
ventilation function of COPD patients, reduced the acute exacerbation rate and
improved the blood gas levels compared with the usual care (P <0.05).
Conclusion: The
extended care improves the quality of life, respiratory function and the mental
health condition of patients with COPD after discharge, indicating that it
contributes to the disease control of patients with COPD.
Keywords: extended
care, COPD, disease control