110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

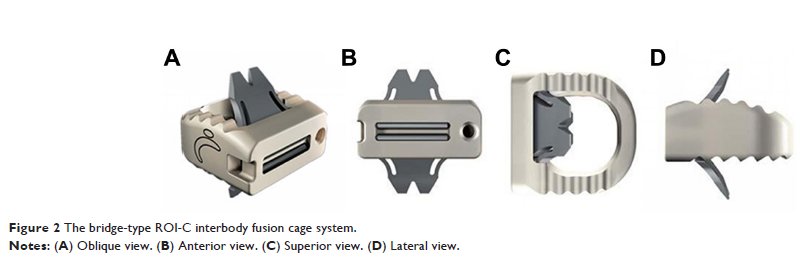
ROI-C 颈椎桥形融合器系统治疗骨质疏松症颈椎病的临床疗效
Authors Rong Y, Luo Y, Liu W, Gong F, Tang P, Cai W
Received 7 August 2018
Accepted for publication 24 October 2018
Published 14 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2543—2551
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S182969
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Objective: To
investigate the early and mid-term efficacy and safety of the bridge-type ROI-C
interbody fusion cage system in the treatment of cervical spondylosis with
osteoporosis during anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF).
Patients and methods: The
clinical data from 24 cervical spondylosis patients with osteoporosis treated
with ACDF were retrospectively analyzed. All patients were treated with ROI-C
cage. Double-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) was used to measure the bone
mineral density (BMD). The cervical sagittal radiographic parameters were measured
and compared using X-ray including C2–C7 Cobb angle, segmental angle (SA),
cervical vertebral bow depth, and height of operation segment (HOS).
Postoperative dysphagia was recorded according to the Bazaz score. The Japanese
Orthopedic Association (JOA) scores and Neck Disability Index (NDI) scores were
used to evaluate the clinical outcomes at different time points. Odom and
Vaccaro criteria were used to assess the surgical effects and to evaluate the
fusion of the bone graft.
Results: The mean
duration of the postoperative follow-up was 27.4±5.7 months (ranging from 21 to
36 months). The JOA scores and NDI scores at 3 months post operation and at the
time of final follow-up were significantly different from those before surgery
(P <0.05). Two
patients had mild dysphagia after surgery, but it disappeared after symptomatic
treatment for 3–5 days. Sagittal radiographic outcomes were significantly
improved at 3 months post operation (P <0.05). At the time of final follow-up, the
radiographic parameters were well maintained and were not significantly
different compared with 3 months post operation (P >0.05).
Conclusion: The ROI-C
cage system is safe and effective for use in patients undergoing anterior
cervical spondylosis surgery for osteoporosis treatment. It results in a
positive effect on bone graft fusion, is able to effectively improve cervical
curvature, restores intervertebral height, and reduces the incidence of
postoperative dysphagia. The clinical effects were positive at the early and
middle postoperative stages.
Keywords: cervical
spondylosis, ROI-C, osteoporosis, imaging parameters, dysphagia