110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利福昔明和乳果糖相结合改善了肝性脑病患者的临床疗效和死亡率
Authors Wang Z, Chu P, Wang W
Received 26 April 2018
Accepted for publication 21 August 2018
Published 17 December 2018 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1—11
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S172324
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Rifaximin
and lactulose are common effective agents for hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Whether
a combination of rifaximin and lactulose improves the efficacy and mortality in
patients with HE compared with lactulose alone needs to be analyzed.
Methods: A
systematic search was performed in electronic databases and other sources for
possible studies focusing on combination therapy of rifaximin and lactulose for
HE between January 2000 and February 2018. A meta-analysis was performed by the
method recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration, and estimated effect size was
presented as risk difference (RD), 95% CI, and the number needed to treat
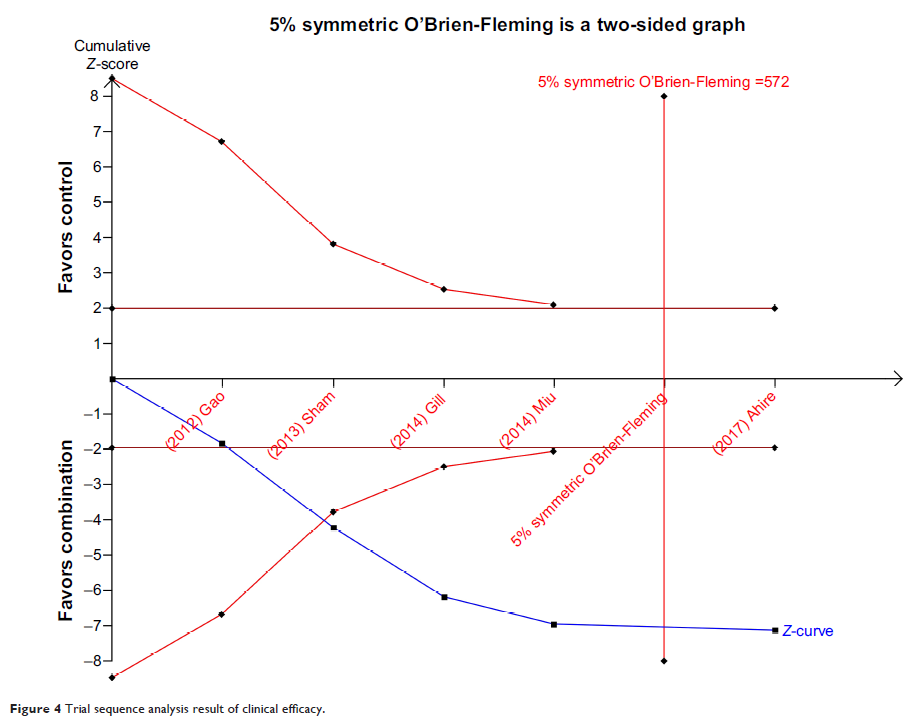
(NNT). Subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and Trial Sequence Analysis
were comprehensively performed to indicate the source of heterogeneity and risk
of bias.
Results: Five
randomized and five observational studies involving 2,276 patients were
included. Combination therapy had a significant advantage in both clinical
efficacy increase (RD 0.26, 95% CI 0.19–0.32, NNT 5) and mortality decrease (RD
-0.16, 95% CI -0.20–0.11, NNT 9) in overall analysis. In the pooled analysis of
randomized studies, combination therapy showed similar results in clinical
efficacy (RD 0.25, 95% CI 0.16–0.35, NNT 4) and mortality (RD -0.22, 95% CI
-0.33–0.12, NNT 5). Compared with lactulose, hospital stay was also reduced in
combination therapy, and there was no significant difference in
treatment-related adverse events between the two groups.
Conclusion: Combination
of rifaximin and lactulose has beneficial effects on HE. Compared with
lactulose alone, additional rifaximin increases clinical efficacy and decreases
mortality. However, its effects on different types of HE are still uncertain.
Keywords: rifaximin,
lactulose, combination therapy, HE, meta-analysis