110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

侵袭性乳腺癌中 ceRNA 网络的构建和分析:一项基于癌症基因组图谱的研究
Authors Gao C, Li H, Zhuang J, Zhang H, Wang K, Yang J, Liu C, Liu L, Zhou C, Sun C
Received 3 August 2018
Accepted for publication 24 October 2018
Published 17 December 2018 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1—11
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S182521
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Studies have
shown that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) make up the major proportion of the
ceRNA network and can regulate gene expression by competitively binding to
miRNAs. This reveals the existence of an RNA-miRNA regulatory pathway and is of
great biological significance. CeRNAs, as competitive endogenous RNAs, have
revealed a new mechanism of interaction between RNAs. Until now, the role of
lncRNA-mediated ceRNAs in breast cancer and their regulatory mechanisms have
been elucidated to some extent.
Purpose: In
this study, comprehensive analysis of large-scale invasive breast cancer
samples in TCGA were conducted to further explore the developmental mechanism
of invasive breast cancer and the potential predictive markers for invasive
breast cancer prognosis in the ceRNA network.
Methods: Abnormal
expression profiles of invasive breast cancer associated mRNAs, lncRNAs and
miRNAs were obtained from the TCGA database. Through further alignment and
prediction of target genes, an abnormal lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network was
constructed for invasive breast cancer. Through the overall survival analysis,
Identification prognostic biomarkers for invasive breast cancer patients,In addition, we used Cytoscape plug-in BinGo for the
different mRNA performance functional cluster analysis.
Results: Differential
analysis revealed that 1059 lncRNAs, 86 miRNAs, and 2138 mRNAs were
significantly different in invasive breast cancer samples versus normal
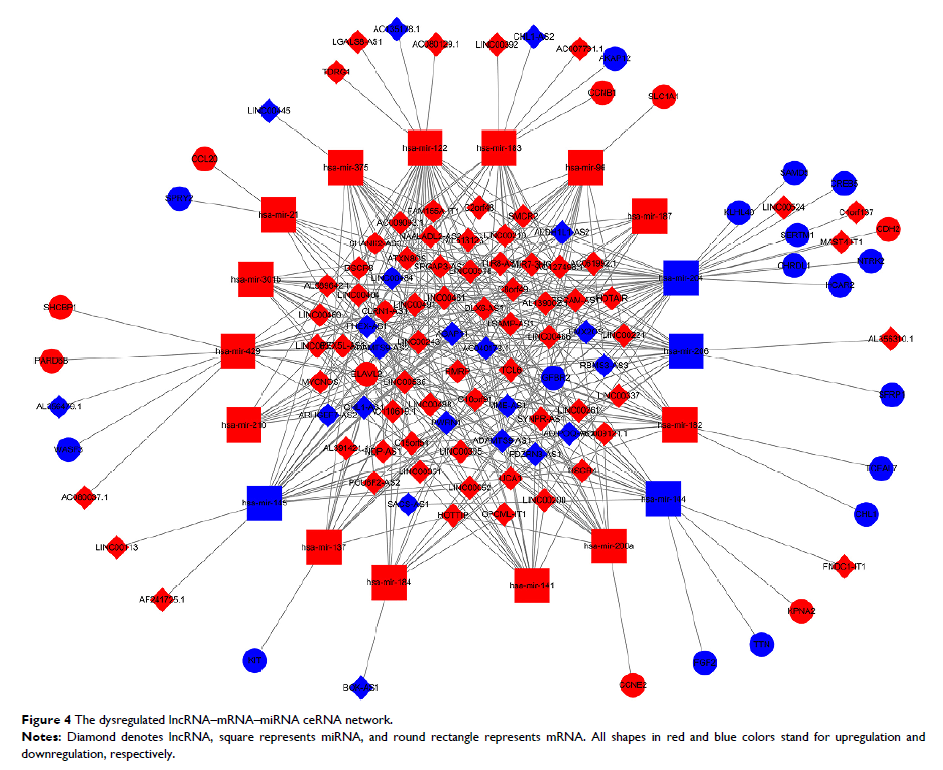
samples. Then we construct an abnormal lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network for
invasive breast cancer, consisting of 90 DElncRNAs, 18 DEmiRNAs and 26
DEmRNAs.Further, 4 out of 90 lncRNAs, 3 out of 26 mRNAs, and 2 out of 18 miRNAs
were useful as prognostic biomarkers for invasive breast cancer patients (P value < 0.05). It is worth noting that based on the ceRNA network, we found
that the LINC00466-Hsa-mir-204- NTRK2 LINC00466-hsa-mir-204-NTRK2 axis was
present in 9 RNAs associated with the prognosis of invasive breast
cancer.
Conclusion: This
study provides an effective bioinformatics basis for further understanding of
the molecular mechanism of invasive breast cancerand for predicting outcomes,
which can guide the use of invasive breast cancerdrugs and subsequent related
research.
Keywords: invasive
breast cancer, cancer genome atlas, lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network,
bioinformatics, diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers