110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

循环 miR130a 的上调与 Barrett 食管和食管腺癌的发展相关
Authors Wang L, Ji F, Liu G, Wang W, Li Z, Yue Y, Wang Z
Received 15 January 2018
Accepted for publication 21 September 2018
Published 17 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1—7
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S162603
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Background: Barrett’s
esophagus (BE) is one of the major known risk factors for esophageal
adenocarcinoma (EAC). Circulating miRNAs are emerging as predictive biomarkers
for early detection of malignancy. However, the potential for circulating
miRNAs to be used as biomarkers for BE neoplastic progression to EAC has not
been well characterized.
Method: We
performed a systematic screening approach to identify spectrum miRNAs in the
serum of both BE and EAC patients.
Results: miRNA-array
web-based software identified 116 sequences differentially expressed between BE
patients and healthy controls. Subsequent study revealed that miR130a was
significantly upregulated in serum samples of BE and EAC patients compared to
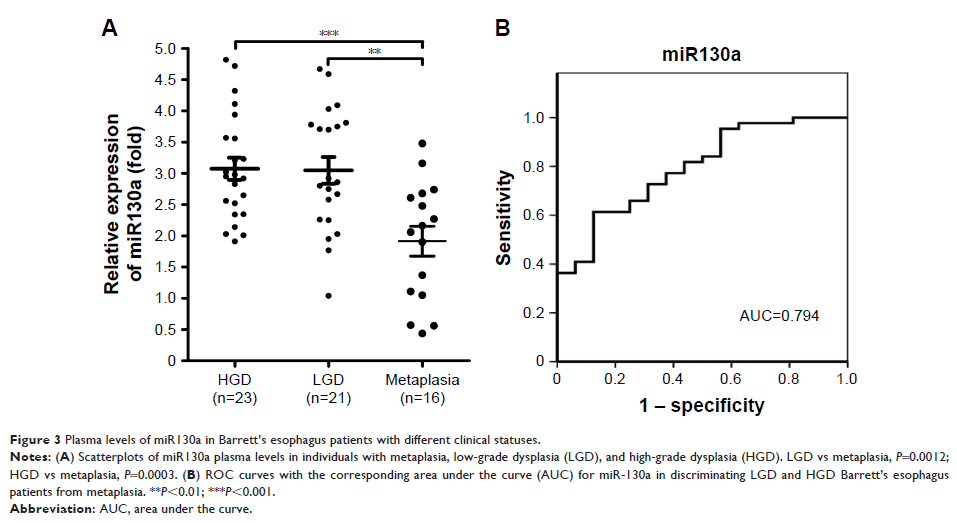
healthy controls. We found an increase in serum miR130a in low-grade and
high-grade dysplasia BE patients compared to individuals with metaplasia. We
also observed that miR130a expression levels increased gradually from
early-stage (I, II) to advanced-stage (III, IV) EAC patients.
Conclusion: Our
preliminary results provide evidence that circulating miR130a is correlated
with the development of BE and EAC.
Keywords: Barrett’s
esophagus, esophageal adenocarcinoma, microRNA, miR130a, biomarker