110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

健脾止痛汤调节谷氨酸转运体的表达,减轻谷氨酸兴奋毒性,并在抽动秽语综合征模型大鼠中发挥抗抽搐作用
Authors Yu W, Shi X, Cui X, Niu Y, Zhang W, Bai X, Wang Q, Hu L, Wang S
Received 24 August 2018
Accepted for publication 30 October 2018
Published 17 December 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 3381—3392
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S185169
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
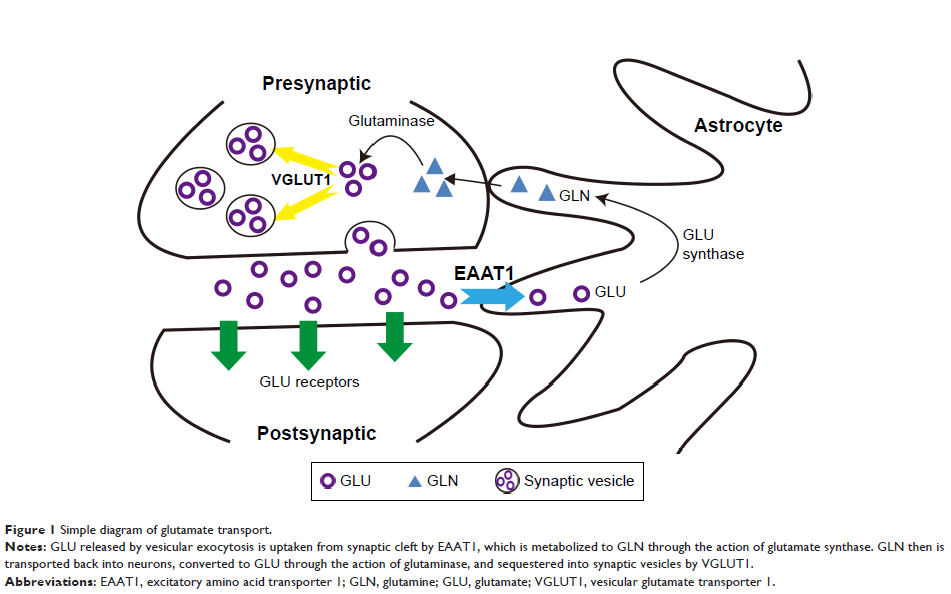
Purpose: This
study explored whether Jian-Pi-Zhi-Dong-Decoction (JPZDD) could regulate the
metabolism of glutamate (GLU) and its transporters in the striatum to exert
anti-tics effects in Tourette syndrome (TS) rats.
Materials and methods: We randomly
assigned 56 Sprague Dawley rats into four groups, each with 14 rats: control,
model, tiapride (Tia), and JPZDD. TS groups (model, Tia, and JPZDD) received
intraperitoneal injection of 3,3'-iminodipropionitrile for 7 days to establish
TS model. Thereafter, rats in the four groups were treated differently once a
day for 6 weeks. Behavioral evaluation was performed each week by using
stereotypy recording and autonomic activity test. The level of GLU in the
striatum was examined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Expression of
EAAT1 and VGLUT1 were measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and
laser scanning confocal microscope.
Results: Compared with
the model group, the stereotypy score and autonomic activity were decreased in
Tia and JPZDD groups. Notably, the model group had increased concentration of
GLU, which decreased after JPZDD and Tia treatments. In the model group, EAAT1
and glial cells were highly co-expressed and the relative fluorescence
intensity (FI) of EAAT1 was significantly lower than that in the control group.
Treatment with JPZDD and Tia increased the relative FI of EAAT1. The mRNA level
of EAAT1 decreased in the model group compared to that in the control group,
although it was significantly elevated following JPZDD or Tia treatment. In the
model group, there was low co-expression of VGLUT1 and axon cells and the FI of
VGLUT1 was remarkably increased relative to that in the control group and
reduced following treatment with JPZDD and Tia. A similar trend was observed in
the mRNA and protein expression of VGLUT1, although it was not statistically
significant.
Conclusion: The mechanism
by which JPZDD alleviated behavioral dysfunction of TS rats may be associated
with maintaining normal GLU transport by upregulating EAAT1 and downregulating
VGLUT1 in the striatum.
Keywords: Jian-Pi-Zhi-Dong-Decoction,
Tourette syndrome, glutamate, EAAT1, VGLUT1