110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

非小细胞肺癌对 T790M 特异性 EGFR 抑制剂奥希替尼出现耐药性后,新出现的获得性 EGFR 外显子 18 G724S 突变:一份病例报告
Authors Zhang Y, He B, Zhou D, Li M, Hu C
Received 25 September 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 18 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 51—56
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S188612
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: T790M mutation
is well known as the most common mechanism for resistance to the first- and
second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for EGFR mutation in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Several third-generation EGFR TKIs, such as
osimertinib, have been explored and approved for conquering this resistance;
however, acquired resistance to osimertinib is evident and the resistance
mechanisms remain complex and incompletely explored.
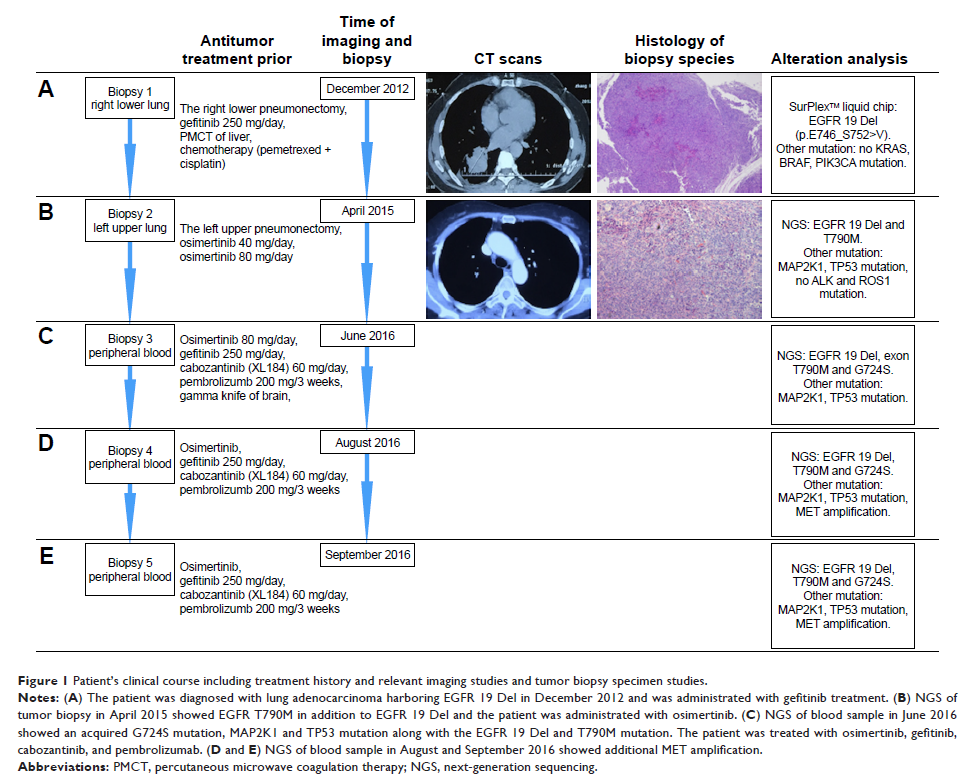
Case presentation: A
non-smoking 58-year-old female patient was initially diagnosed with lung
adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR exon 19 deletion and clinically responded to
initial gefitinib treatment. The patient progressed on gefitinib after >1
year and a T790M mutation was detected in tissue biopsy by next-generation
sequencing (NGS). Osimertinib treatment was administrated for several months
and an acquired rare EGFR G724S mutation was detected via NGS blood sample
after osimertinib resistance.
Conclusion: The
specific mechanisms of acquiring drug resistance for EGFR-TKIs have not been
fully explored. EGFR G724S mutation might be associated with osimertinib
resistance but more studies about the mechanism should be explored.
Keywords: NSCLC, EGFR
mutation, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, next-generation sequencing