110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

患者控制的静脉曲马多与患者控制的静脉氢吗啡酮用于继发剖宫产术后镇痛的对比:一项随机对照试验用于比较镇痛、抗焦虑和抗抑郁作用
Authors Duan G, Bao X, Yang G, Peng J, Wu Z, Zhao P, Zuo Z, Li H
Received 21 August 2018
Accepted for publication 22 November 2018
Published 18 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 49—59
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S184782
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Ueberall
Introduction: This study
aimed to compare the postoperative analgesic effects of tramadol and
hydromorphone for secondary cesarean delivery (CD) as well as their
anti-anxiety and anti-depression properties.
Methods: A
total of 106 patients receiving secondary CD under spinal anesthesia were
randomly allocated to the tramadol group (n=53) and the hydromorphone group
(n=53). Each group received patient-controlled intravenous analgesia using
flurbiprofen 4 mg/kg combined with tramadol (4 mg/kg) or hydromorphone
(0.04 mg/kg) immediately after the surgery. Postoperative pain numerical
rating scale (NRS) for incision and visceral pain, hospital anxiety and
depression scale (HADS), early walking time and length of hospital stay were
assessed.
Results: Patients
in the tramadol and hydromorphone groups exhibited equivalent incision pain NRS
at different time points (P >0.05). Visceral pain in the tramadol group was
higher than that in the hydromorphone group at postoperative 4 hours (2.9 [1.2]
vs 2.3 [1.4], P =0.011) and 8 hours (2.4 [1.1] vs 1.8
[1.1], P =0.028).
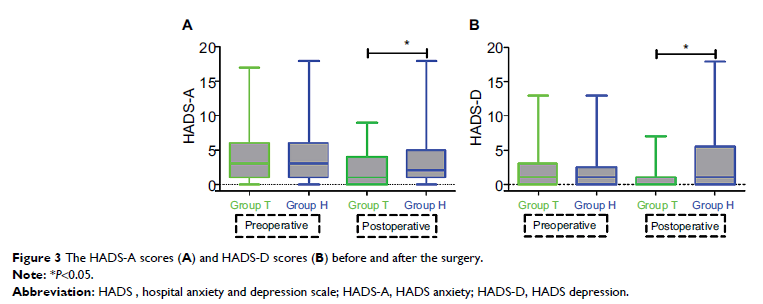
One week after the surgery, the patients in the tramadol group, as compared to
the hydromorphone group, had lower anxiety scores (1.9 [3.5] vs 3.6
[4.1], P =0.033)
and depression scores (0.8 [1.3] vs 2.7 [4.1], P =0.023). In
addition, early walking time (25.3 [7.0] hours vs 29.3 [9.6] hours, P =0.016) and length
of hospital stay (2.9 [0.8] days vs 3.3 [0.8] days, P = 0.008) after the
surgery in the tramadol group were less than those in the hydromorphone group.
Conclusion: Postoperative intravenous analgesia with tramadol or hydromorphone for
secondary CD provides comparable analgesic effects on incision pain. Tramadol
is less effective in controlling visceral pain compared to hydromorphone.
However, tramadol can help to alleviate anxiety and depression in the early
postpartum period, improve patients’ early mobilization and shorten their
hospital stay.
Clinical trial number and registry URL: No: ChiCTR-IIR-17011043; URL: www.chictr.org.cn.
Keywords: anxiety,
caesarean section, depression, postoperative pain, tramadol