110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

骨髓间充质干细胞衍生外泌体对激素性股骨头坏死的成骨作用
Authors Fang S, Li Y, Chen P
Received 29 June 2018
Accepted for publication 22 November 2018
Published 18 December 2018 Volume 2019:13 Pages 45—55
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S178698
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
Background: Animal studies
have demonstrated the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on
osteogenesis, but little is known about the functions of exosomes (Exos)
released by bone MSCs (BMSCs). Here, we investigated the effect of BMSC Exos on
steroid-induced femoral head necrosis (SFHN) and explored the vital genes
involved in this process.
Materials and methods: BMSCs
were isolated from healthy and SFHN rats. BMSC Exos were isolated using the
Exosome Precipitation Kit and characterized by transmission electron microscopy
and Western blotting. SFHN BMSCs were incubated with Exos from healthy BMSCs.
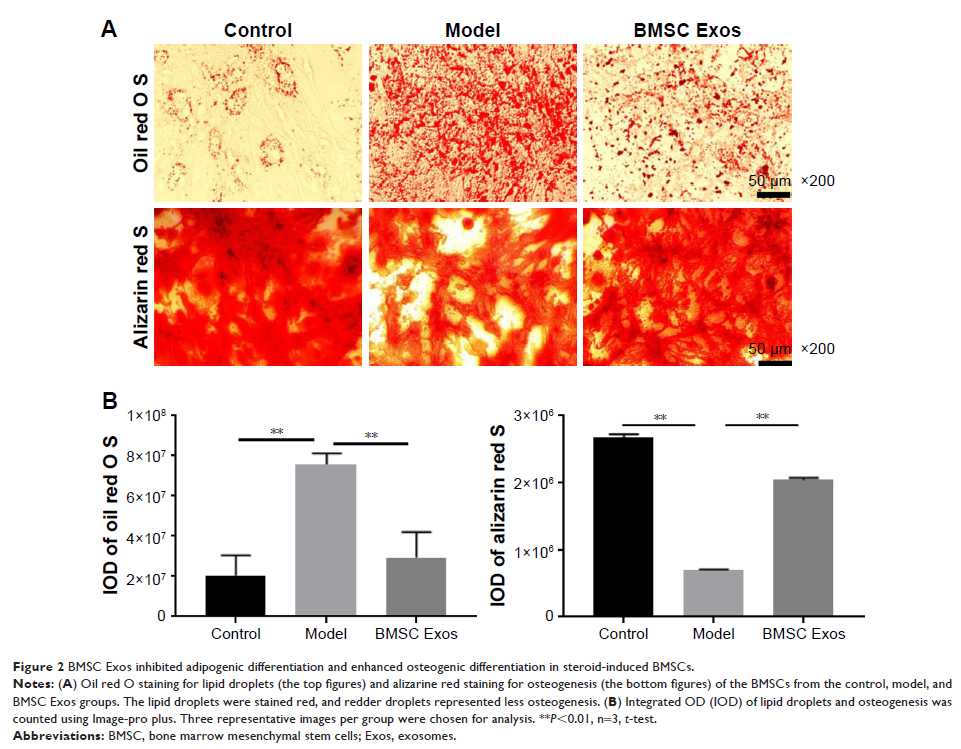
Osteogenic ability was assessed by oil red O staining and alizarine red
staining. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) induced by Exos were screened
using the Osteogenesis RT2 Profiler PCR Array. The effect of
upregulated Sox9 was examined using lentivirus-mediated
siRNA.
Results: The results
revealed that BMSC Exos were 100–150 nm in size and expressed CD63. Moreover,
BMSC Exo-treated SFHN cells exhibited suppressed adipogenesis compared to model
cells. PCR array showed that eleven and nine genes were upregulated and
downregulated, respectively, in the BMSC Exo-treated SFHN cells compared to the
model group. Among the DEGs, osteogenesis-related genes, including Bmp2 , Bmp6 , Bmpr1b , Mmp9 , and Sox9 , may play
important roles in SFHN. Furthermore, the DEGs were mainly involved in immune
response, osteoblast differentiation, and in the transforming growth
factor-β/bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. The level of the SOX9
protein was upregulated by Exos, and Sox9 silencing significantly decreased the
osteogenic effect of BMSC Exos.
Conclusion: Our data
suggest that Exos derived from BMSCs mainly affect SFHN osteogenesis, and this
finding can be further investigated to develop a novel therapeutic agent for
SFHN.
Keywords: exosome, bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells, steroid-induced femoral head necrosis, gene
expression, ostosis