110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA SNHG15 充当癌基因并可预测上皮性卵巢癌的不良预后
Authors Qu C, Dai C, Guo Y, Qin R, Liu J
Received 5 August 2018
Accepted for publication 27 October 2018
Published 19 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 101—111
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182657
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: This study aims
to investigate the functional role of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 in epithelial
ovarian cancer (EOC).
Materials and methods: The expression
of SNHG15 was measured in EOC cells and tissues using qRT-PCR. The correlation
of SNHG15 expression and the clinicopathological characters was statistically
analyzed. The prognosis of patients with different clinical features in the
high/low SNHG15 expression groups were calculated. Moreover, univariate and
multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to identify the risk
factors for poor overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). The
effect of SNHG15 on the migration and invasion was evaluated using Transwell
and Matrigel, respectively. The proliferation ability of EOC cells was tested
using colony formation and MTT assay. The influence of SNHG15 on the cisplatin
resistance was detected by measuring cell inhibition rate and cell viability.
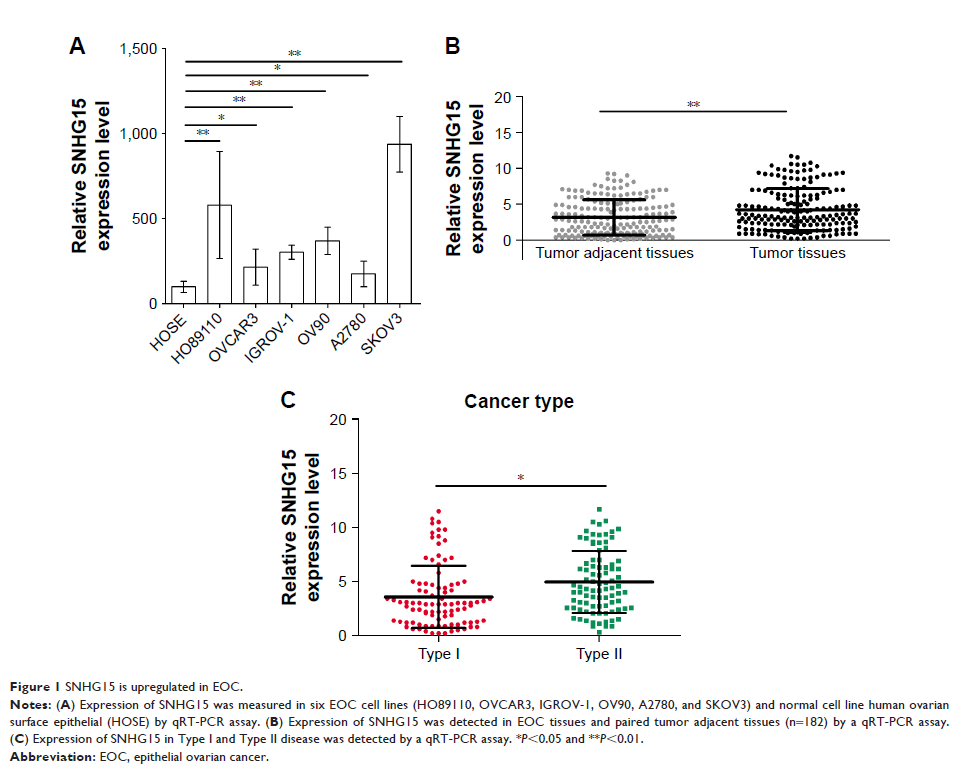
Results: SNHG15 was
upegulated in EOC cells and tissues. High SNHG15 expression was correlated with
EOC progression and predicted poor OS and PFS in different subgroups of EOC
patients. Moreover, multivariate Cox regression analysis defined high SNHG15
expression as an independent risk factor for poor OS and PFS. Furthermore,
functional assays showed that the overexpression of SNHG15 promoted migration
and invasion, while the loss of SNHG15 suppressed migration and invasion.
Furthermore, the proliferation of EOC cells was improved after the ectopic
expression of SNHG15, which was suppressed with SNHG15 deficiency. In addition,
cisplatin-resistant EOC cells were established for detecting the effect of SNHG15
on EOC chemoresistance. The results showed that cisplatin-resistant EOC cells
exhibited much higher levels of SNHG15 expression than controls, and SNHG15
contributed to the chemoresistance of EOC cells.
Conclusion: This
study confirms that SNHG15 contributes to the migration, invasion,
proliferation, and chemoresistance of EOC. SNHG15 may serve as a potential
therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker of EOC patients.
Keywords: noncoding
RNA, ovarian cancer, proliferation, metastasis, chemoresistance