110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肉毒杆菌毒素可缓解面肌痉挛和眼睑痉挛患者的焦虑和抑郁
Authors Dong H, Fan S, Luo Y, Peng B
Received 29 July 2018
Accepted for publication 27 October 2018
Published 19 December 2018 Volume 2019:15 Pages 33—36
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S181820
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Papan Thaipisuttikul
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Objective: To
explore the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) therapy in relieving
anxiety and depression in patients with hemifacial spasm (HFS) and benign
essential blepharospasm (BEB).
Patients and method: Ninety
idiopathic HFS patients and 90 BEB patients were enrolled. The anxiety and
depression status were evaluated by self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and
self-rating depression scale (SDS), respectively, before and after the
injection of BTX-A.
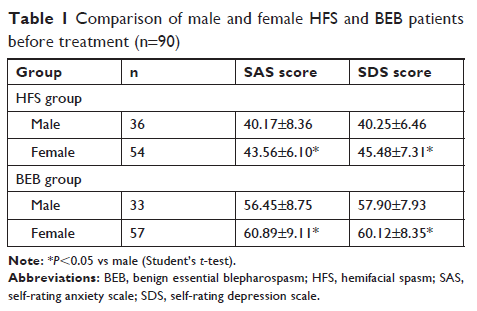
Results: Before
treatment, the SAS and SDS scores of HFS patients were 41.25±6.35 and
42.25±7.57, respectively. The SAS scores were 40.17±8.36 for males and
43.56±6.10 for females (P =0.031). The SDS scores were 40.25±6.46 for males and
45.48±7.31 for females (P =0.008). After treatment, the SAS and SDS scores were
30.12±4.35 and 30.58±4.89, respectively. There was a significant difference in
the SAS and SDS scores before and after treatment. Before treatment, the SAS
scores of male and female BEB patients were 56.45±8.75 and 60.89±9.11,
respectively, and the SDS scores of male and female BEB patients were
57.90±7.93 and 60.12±8.35, respectively. After treatment, the SAS score was 38.17±3.67
and the SDS score was 38.12±4.15, with a significant difference in before and
after treatment scores.
Conclusion: In HFS
and BEB, especially in female patients, there is an association with anxiety
and depression. BTX-A can improve the symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Keywords: hemifacial
spasm, blepharospasm, anxiety, depression, botulinum toxin type A