110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

盐酸小檗碱与辛伐他汀和非诺贝特的药代动力学相互作用和耐受性:一项针对健康中国志愿者的开放标签、随机、平行研究
Authors Li G, Zhao M, Qiu F, Sun Y, Zhao L
Received 27 August 2018
Accepted for publication 21 November 2018
Published 20 December 2018 Volume 2019:13 Pages 129—139
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S185487
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: Fenofibrate
(Fbt) is a prodrug that has been used to reduce low-density-lipoprotein
cholesterol, triglycerides, and increase high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol.
Simvastatin (Svt) is a classic lipid-lowering drug that is widely used in the
treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia, while berberine
chloride (Bbr) is a novel hypolipidemic agent and its blood-lipid-reducing
mechanism is distinct from traditional drugs. Currently, drug combination is
the trend in treating hyperlipidemia to improve clinical efficacy. The purpose
of this study was to evaluate drug interaction from the perspective of
pharmacokinetics between Bbr and Fbt/Svt and the tolerability of combined
administration in healthy Chinese subjects.
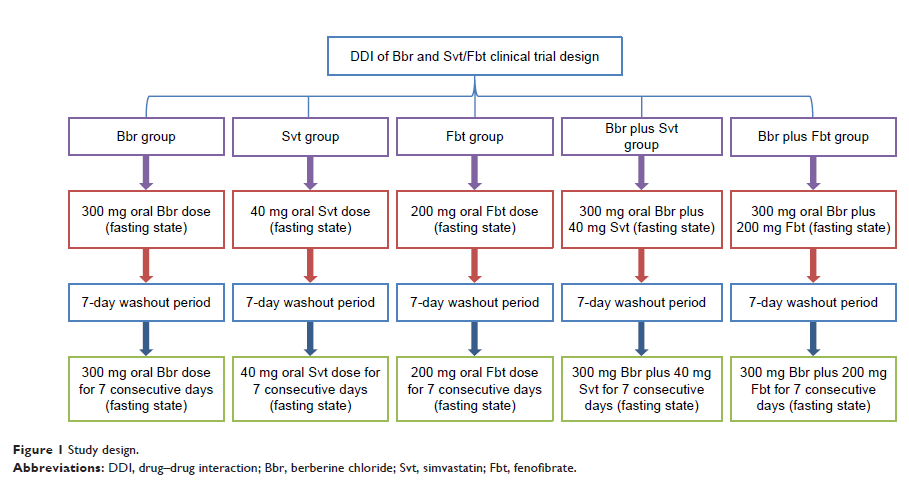
Methods: Healthy
subjects (n=60) were randomly allocated to five treatment groups: Bbr alone,
Fbt alone, Svt alone, Bbr plus Fbt, and Bbr plus Svt. The experiment was
divided into two parts: single-dose administration and multiple-dose
administration. Bbr, Fbt, and Svt were taken once every 8 hours, 24 hours, and
24 hours, respectively, over 7 days in the multidose group. Plasma samples were
collected and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry was
used to detect drug concentrations.
Results: No
serious adverse reactions or intolerance were observed throughout the trial.
More importantly, the combined-administration groups did not show an increase
in incidence of side effects. Coadministration of Fbt and Svt with Bbr had no
significant effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of Bbr, except time to maximum
concentration, apparent volume of distribution, and apparent clearance.
Concurrent coadministration of Bbr had no obvious impact on the pharmacokinetic
behavior of Fbt or Svt. Additionally, there was no significant correlation
between sex and pharmacokinetic results.
Conclusion: All
treatments were well tolerated. No clinically obvious pharmacokinetic
interactions between Bbr and Fbt/Svt were observed with combined
administration. The results demonstrated that Bbr can be coadministered safely
with Fbt and Svt without dose adjustment.
Keywords: Bbr, Fbt,
Svt, drug–drug interaction, pharmacokinetics