110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

靶向 CDC7 可提高食管鳞状细胞癌对化疗的敏感性
Authors Cao JX, Lu Y
Received 12 August 2018
Accepted for publication 16 November 2018
Published 20 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 63—74
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S183629
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: The cell
division cycle 7 (CDC7) is a serine/threonine kinase that is essential for DNA
replication in human cells which has been identified to play a critical role in
multiple cancer types. However, the expression and clinical significance of
CDC7 in ESCC has never been reported.
Patients and methods: CDC7
expression was detected in 30 ESCC and matched adjacent normal tissues, and a
series of loss-of-function and gain-of-function assays were performed to
evaluate the effects of CDC7 on the proliferation, migration and invasion, and
chemoresistance of ESCC cells.
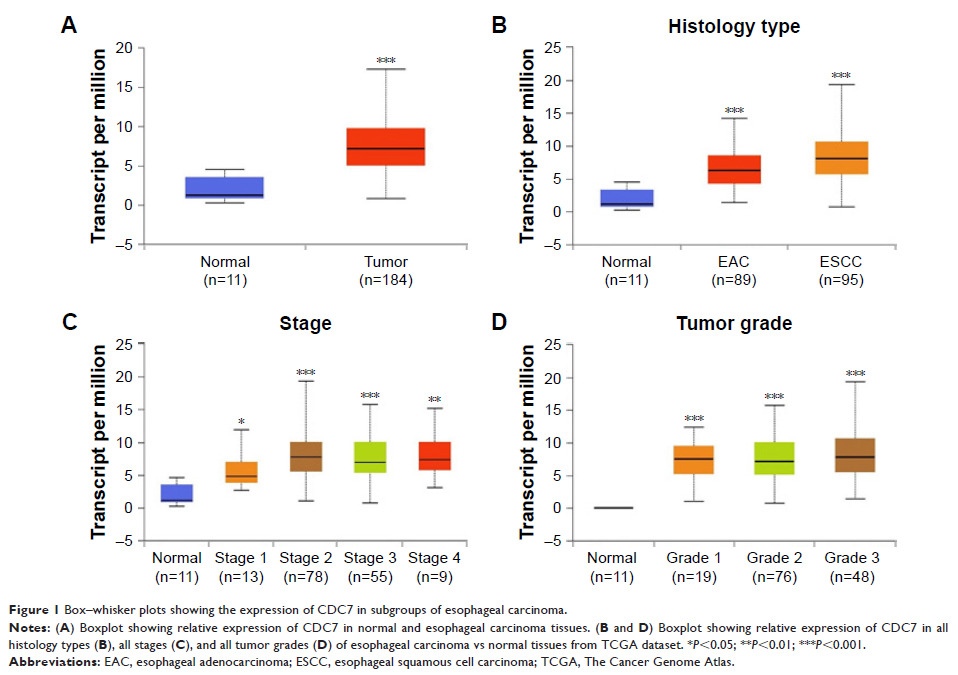
Results: The results
showed that CDC7 was highly expressed in ESCC tissues compared with matched
adjacent normal tissues. Functional studies demonstrated that knockdown of CDC7
inhibited proliferation by arresting ESCC cells in the G0/G1 phase and inducing
apoptosis. Knockdown of CDC7 also inhibited cell migration and invasion in ESCC
cells. Furthermore, knockdown of CDC7 sensitized ESCC cells to Cis and 5-FU.
Conclusion: Our
results suggest that CDC7 is highly expressed in ESCC tissues, and silencing
CDC7 enhances chemosensitivity of ESCC cells, providing a new avenue for ESCC
therapy.
Keywords: CDC7, ESCC,
chemosensitivity, therapeutic target, proliferation, migration and invasion