110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

厄贝沙坦和氢氯噻嗪的短期治疗可降低 COPD 急性加重患者的血浆 N 末端脑钠尿肽水平
Authors Jiang GY, Li Q, Lv YX
Received 10 September 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 20 December 2018 Volume 2019:14 Pages 73—80
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S186872
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Chunxue Bai
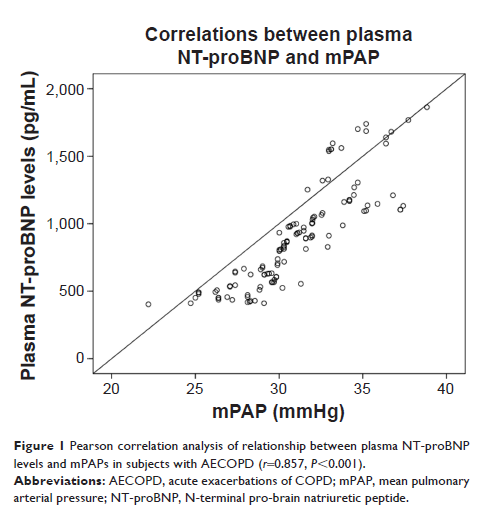
Background: Plasma levels
of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are elevated in
subjects with COPD, and high plasma NT-proBNP levels are correlated with a poor
prognosis. Thus, it is crucial to decrease the plasma NT-proBNP levels at the
early stage of disease. We aimed to assess the effects of short-term treatment
of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide on plasma NT-proBNP levels and
health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in subjects with acute exacerbations of
COPD (AECOPD).
Subjects and methods: Eighty subjects
with AECOPD and high plasma NT-proBNP levels, without any clinical evidence of
cor pulmonale, were enrolled. The subjects were randomly allocated into two
groups of 40 subjects. In addition to standard treatment for AECOPD, the
subjects in group I were treated with irbesartan alone, and those in group II
were treated with irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide for a week. Forty subjects
with stable COPD were enrolled as a control group. Plasma NT-proBNP
concentrations were measured on admission and on the first, fourth, and seventh
days. The subjects’ health-related quality of life was evaluated applying the
36-item short-form questionnaire on the first day before treatment and on the
seventh day after treatment.
Results: Treatment of
irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide significantly decreased plasma NT-proBNP
levels in subjects with AECOPD, and this reduction was more significant in
group II than that in group I. There were no significant differences in 36-item
short-form domain scores between subjects with stable COPD and those with AECOPD
who were treated with irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide.
Conclusion: Treatment of
irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide rapidly decreased plasma NT-proBNP levels in
subjects with AECOPD, and the treatment did not impair their physical status.
Keywords: COPD,
health-related quality of life, hydrochlorothiazide, irbesartan, NT-proBNP