110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

香烟烟雾诱导的 RANKL 表达可增强肺泡巨噬细胞的 MMP-9 产生
Authors Zhou L, Le Y, Tian J, Yang X, Jin R, Gai X, Sun Y
Received 7 October 2018
Accepted for publication 29 November 2018
Published 20 December 2018 Volume 2019:14 Pages 81—91
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S190023
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Chunxue Bai
Background and purpose: Cigarette
smoke (CS) induces alveolar destruction through overproduction of proteinases
including matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 by alveolar macrophages (AMs). Receptor
activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) functions in immune regulation
and cytokine secretion; whether it is involved in CS-induced MMP-9 expression
is unknown. The purpose of our study was to investigate the expression and
functional role of RANKL pathway in MMP-9 production pertaining to the
pathogenesis of COPD.
Materials and methods: We first
localized RANKL and its receptor RANK in the lungs of mice exposed to long-term
CS exposure. Next, we studied RANKL and RANK expression under CS extract (CSE)
stimulation in vitro. Lastly, we studied the in vitro biological function of
RANKL in CS-induced production of MMP-9.
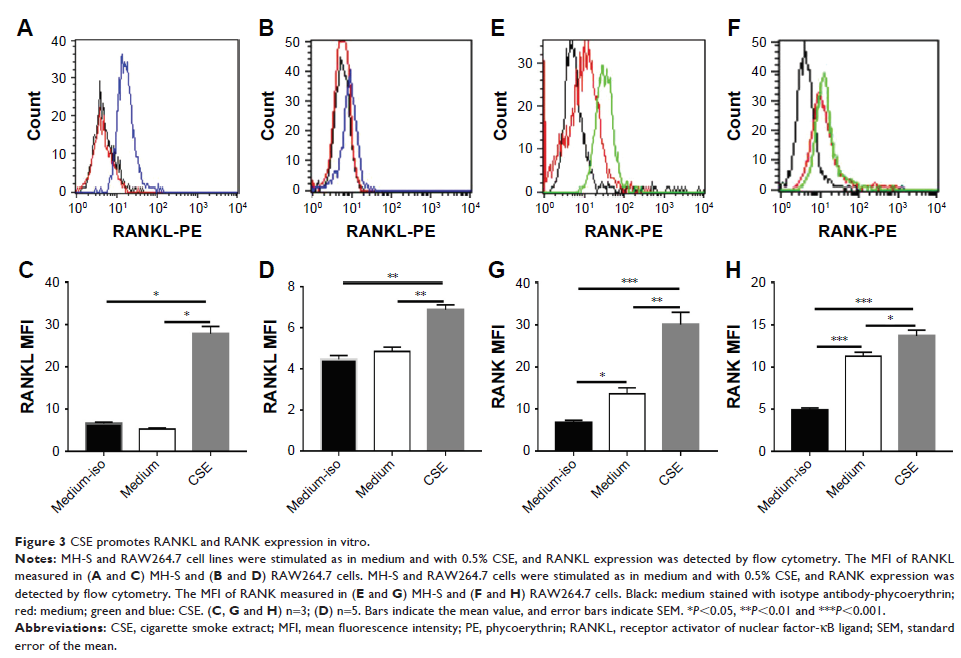
Results: Both RANKL and
RANK were highly expressed in AMs in CS-exposed mice, but not in the control
mice. In vitro, CSE increased the expressions of RANKL and RANK in macrophages.
AMs responded to CSE and RANKL stimulation by overexpressing MMP-9, and
CSE-induced MMP-9 expression was partly blocked by using monoclonal anti-RANKL
antibody.
Conclusion: RANKL/RANK
pathway mediates CS-induced MMP-9 expression in AMs, suggesting a novel
mechanism for CS-associated emphysema.
Keywords: COPD, receptor
activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, RANK, alveolar macrophages, MMP-9