110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗颅内动脉瘤破裂后急性血栓栓塞并发症的治疗:一份病例报告
Authors Xu N, Meng H, Liu T, Feng Y, Qi Y, Wang H
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 17 November 2018
Published 21 December 2018 Volume 2019:15 Pages 69—74
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S184372
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
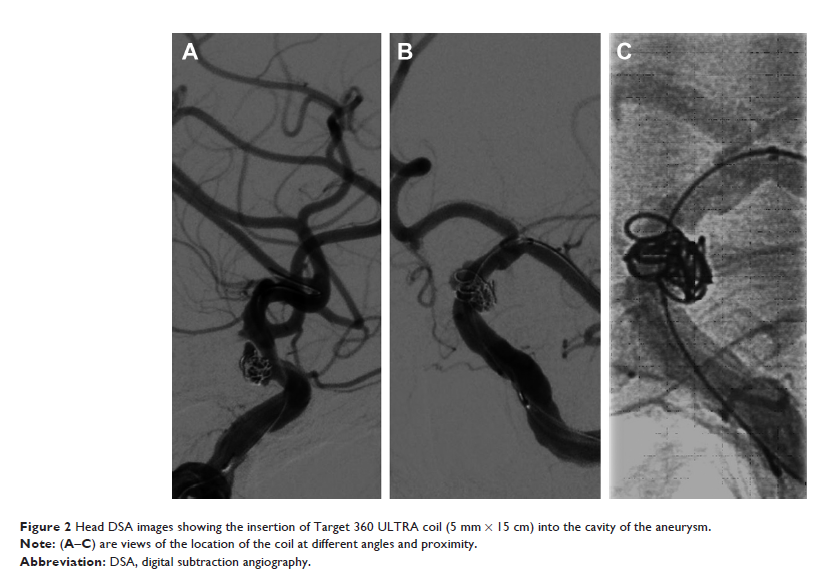
Abstract: A
45-year-old Chinese man presented with acute severe headache for 2 days. He was
diagnosed as subarachnoid hemorrhage. Head CT and subsequent head digital
subtraction angiography (DSA) showed left internal carotid artery (ICA)
aneurysm in the supraclinoid segment. Stent-assisted coil embolization of
aneurysm was performed. Three hours after the surgery, the patient was found to
be drowsy and with paralysis of the right limb and slurred speech. Urgent head
CT examination ruled out acute hemorrhage; however, DSA showed acute thrombosis
in the left ICA between the branches of the ophthalmic artery and middle
cerebral artery, which was probably from an acute in-stent thrombosis.
Urokinase (100,000 units) was given through a micro-tube but failed to dissolve
the thrombus; thus, stent embolectomy was performed, which successfully removed
the thrombus. Repeat angiography showed that the left ICA was completely
recanalized. Postoperatively, the patient regained consciousness and was
well-limbed and fluent in speech. No neurological symptoms or signs were found
at 6-, 12-, and 24-month follow-up.
Keywords: acute
thromboembolic complication, intracranial aneurysm, stent-assisted coil
embolization, re-canalized