110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA PTENP1 的过表达在体外抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖和转移
Authors Hu S, Xu L, Li L, Luo D, Zhao H, Li D, Peng B
Received 3 August 2018
Accepted for publication 18 October 2018
Published 21 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 147—156
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182537
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Glioma is one
of the most common malignancies of the central nervous system in adults. The
lncRNA PTEN pseudogene-1 (PTENP1) has been reported to play an important role
in the development and progression of various cancers. However, the molecular
mechanism by which lncRNA PTENP1 affects the development and progression of
gliomas remains unclear.
Materials and methods: The levels of
PTENP1 expression in glioma tissues and normal brain tissues were detected by
quantitative real-time PCR. Cell Counting Kit-8 and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine
staining assays were performed to detect cell proliferation. Flow cytometry was
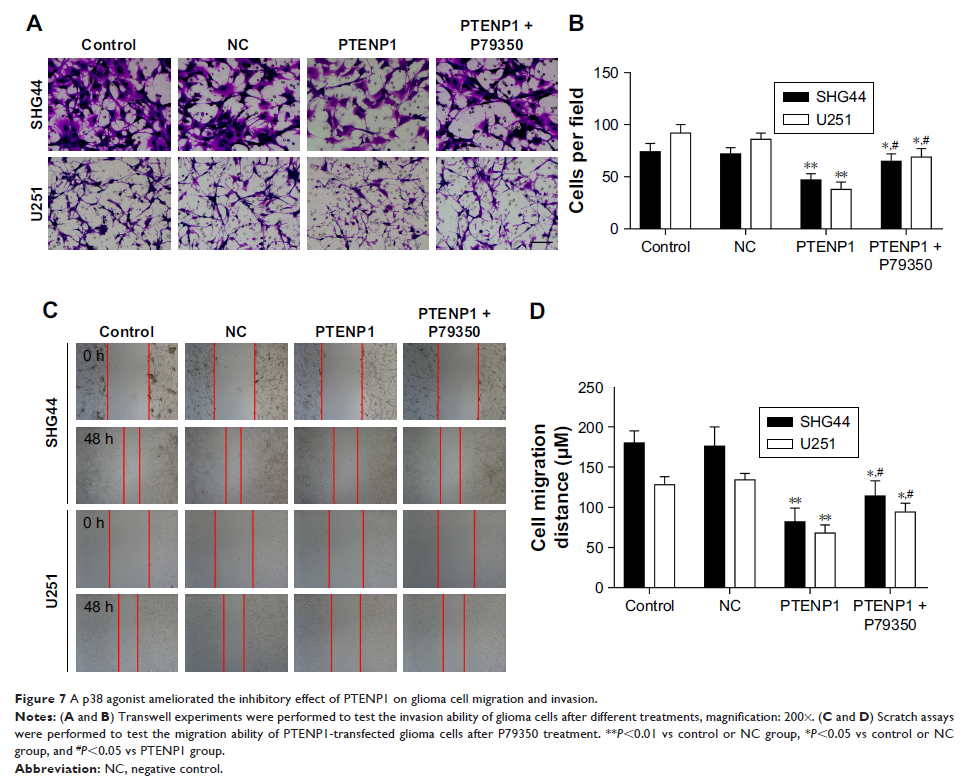
used to analyze cell cycle progression. Transwell assay and scratch test were
used to detect cell migration and invasion, and Western blot studies were
performed to detect protein expression.
Results: Our
results showed that expression of lncRNA PTENP1 was decreased in glioma tissues
when compared with normal brain tissues. Overexpression of PTENP1 suppressed
SHG44 and U251 cell proliferation and significantly decreased the numbers of
S-phase cells. Furthermore, the invasion and migration abilities of SHG44 and
U251 cells were reduced after being transfected with a PTENP1 overexpression
plasmid. Overexpression of PTENP1 induced the expression of p21 protein and
suppressed the p38 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our study
investigated the function of PTENP1 in glioma and provided new insights for
treating that malignancy.
Keywords: lncRNA
PTENP1, glioma, proliferation, invasion, migration