110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA DANCR 通过抑制 p21 表达来促进非小细胞肺癌的进展
Authors Guo L, Gu J, Hou S, Liu D, Zhou M, Hua T, Zhang J, Ge Z, Xu J
Received 5 September 2018
Accepted for publication 26 November 2018
Published 21 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 135—146
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186607
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Long
non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in human cancers. However, the
functional roles of lncRNAs in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and the
underlying mechanisms are not well understood.
Methods: We
examined the expression of lncRNA DANCR in NSCLC by qRT-PCR and explored its
biological roles in NSCLC progression by cell and molecular biology studies.
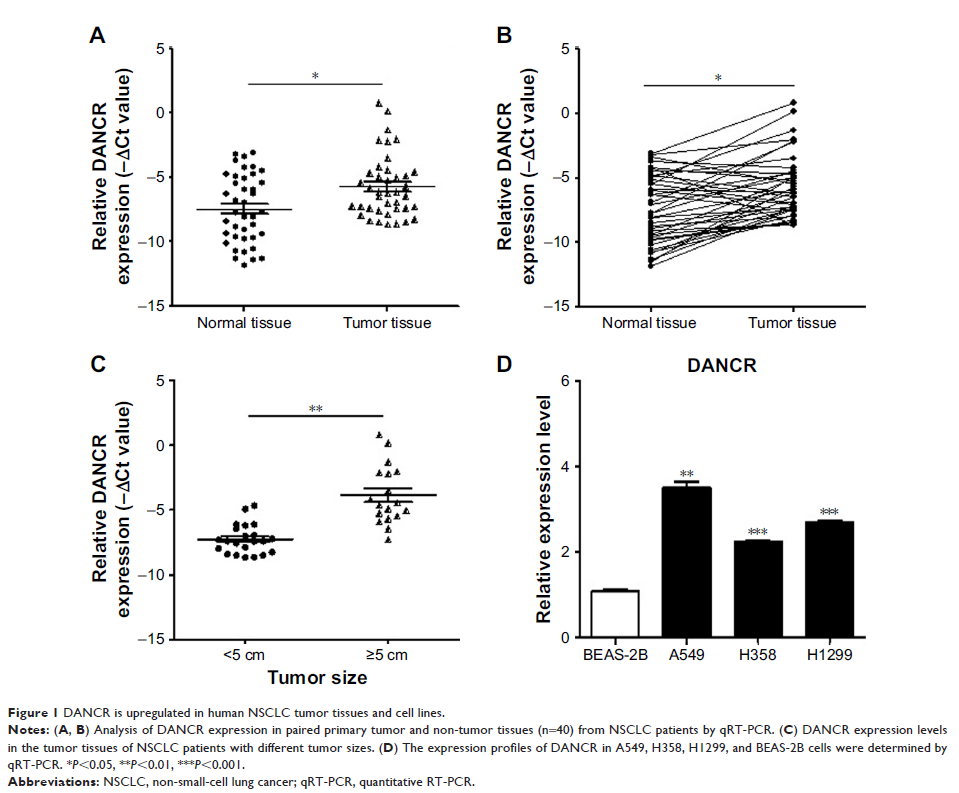
Results: DANCR
expression level was increased in human NSCLC. The knockdown of DANCR inhibited
NSCLC cell proliferation by inducing cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. In
addition, DANCR knockdown suppressed NSCLC cell migration and invasion via
inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). On the contrary, DANCR
overexpression had the opposite effects. DANCR knockdown inhibited
EZH-2-mediated epigenetic silencing of p21 promoter and increased p21
expression. Moreover, DANCR knockdown inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion in a p21-dependent manner.
Conclusion: DANCR
plays oncogenic roles in NSCLC and may provide a novel biomarker for NSCLC
diagnosis and prognosis.
Keywords: DANCR, NSCLC,
progression, biomarker