110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MARCH5 过表达有助于肿瘤生长和转移,并与乳腺癌的生存率低有关
Authors Tang H, Peng S, Dong Y, Yang X, Yang P, Yang L, Yang B, Bao G
Received 12 October 2018
Accepted for publication 19 November 2018
Published 24 December 2018 Volume 2019:11 Pages 201—215
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S190694
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: Human
MARCH5 is a mitochondrial localized E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that is
critical for the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. A body of evidence has
indicated the close links between unbalanced mitochondrial dynamics and
cancers. However, the expression, biological functions, and prognostic
significance of MARCH5 in breast cancer (BC) have not been determined.
Materials and methods: The mRNA and
protein expressions of MARCH5 were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR and
Western blot analysis in BC cell lines and tumor tissues. Clinical prognostic
significance of MARCH5 was assessed in 65 patients with BC. The biological
functions of MARCH5 were determined by in vitro cell proliferation, apoptosis,
cell cycle, migration and invasion assays, and in vivo tumor growth and
metastasis assays through knockdown or overexpression of MARCH5 in BC cells. In
addition, the underlying mechanisms by which MARCH5 regulated BC cell growth
and metastasis were explored.
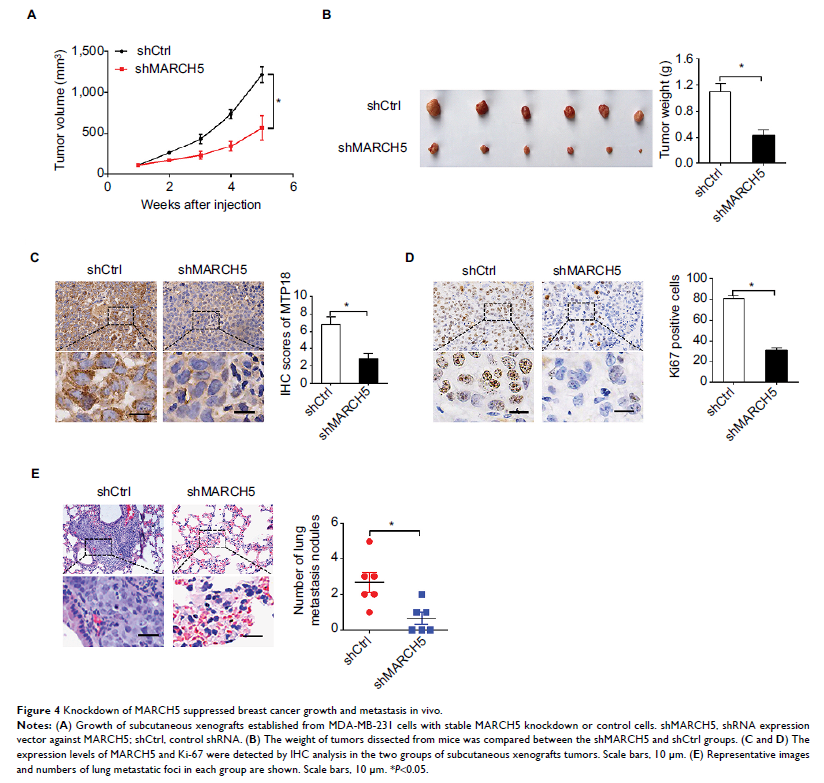
Results: MARCH5 was
substantially upregulated in BC cells mainly due to the downregulation of
miR-30a, which contributed to the poor survival of BC patients. MARCH5 promoted
the growth and metastasis of BC cells both in vitro and in vivo by inducing
G1–S cell cycle arrest and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Mechanistic
investigations revealed that the oncogenic effect of MARCH5 was mainly mediated
by increased mitochondrial fission and subsequent ROS production in BC cells.
Conclusion: Our
findings demonstrate that MARCH5 plays a critical oncogenic role in BC cells,
which provides experimental evidence supporting MARCH5 as a potential
therapeutic target in BC therapy.
Keywords: MARCH5,
proliferation, invasion, prognosis, BC