110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

参加或完成针灸试验的态度和参与意愿:一个横断面研究
Authors Li X, Cao H, Zhang Y, Hu R, Lai B, Zhao N, Hu H, Xie Z, Liu JP
Received 5 May 2018
Accepted for publication 30 August 2018
Published 24 December 2018 Volume 2019:13 Pages 53—61
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S173202
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 7
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Objective: To explore
the influence of patients’ participation in and completing the acupuncture
clinical trials through a cross-sectional survey. In addition, we explored
potential factors involved in improving patient’s compliance to treatment, thus
enhancing the quality of acupuncture clinical studies.
Methods: A survey
was conducted at outpatient department of acupuncture and metabolic diseases in
two hospitals in Beijing. The semi-structured questionnaire was designed based
on literature review and Delphi methods. It contains 15 questions related to
patients’ experience and attitude. SPSS 22.0 was used for analyses. OR and 95%
CI were used for dichotomous outcomes. Logistic regression analysis (LRA) and
multi-LRA were used to explore the factors influencing patients’ participation
or completion and the relationship between demographic characteristics and
potential factors.
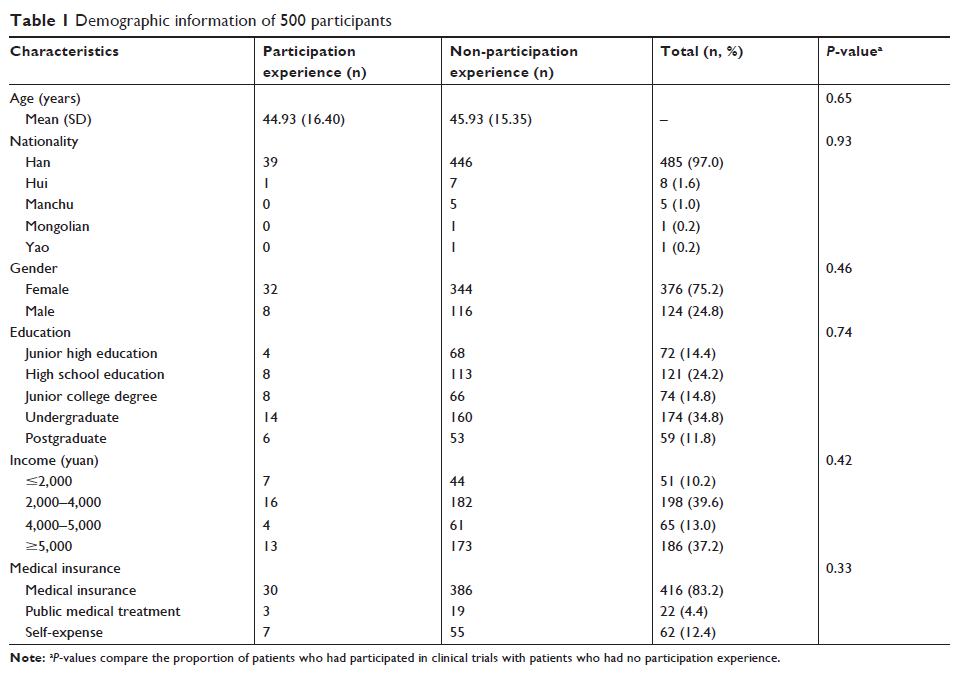
Results: A survey
was conducted from April to September 2016. Five hundred patients were
consecutively sampled to fill semi-structured questionnaires regardless of
their types of disease. The participants (75.2% were female) were in the age
range of 15–85 years and all of them completed the survey. The effect and
safety of acupuncture therapy were considered to be the deciding factors by 92%
and 96% of the respondents, respectively. Only 40 of the surveyed participants
(8.0%) had previously participated in the clinical trials. The LRA showed they
paid more attention to treatment regimen (frequency and session of treatment)
when deciding whether or not to participate in the trials (OR 1.54, 95% CI
1.02–2.34). Multivariate LRA showed that elder people considered cost (OR 1.36,
95% CI 1.09–1.70) to be an important factor, while the participants having
medical insurance (OR 1.45, 95% CI -0.20–0.93) thought informed consent was
important. Meanwhile, participants with higher education preferred regular
follow-up (OR 1.16, 95% CI 0.02–0.28).
Conclusion: After providing
adequate information regarding the potential benefits and harms of the
acupuncture treatment, completion of the treatment within the specific time
regimen was found to be the most important factor affecting patient’s
compliance. Other factors, such as cost and regular follow-up, should also be
given special consideration.
Keywords: patient
compliance, acupuncture, clinical trials, cross-sectional study