110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA SNHG5 通过调节 miR-26a-5p/TRPC3 通路促进黑素瘤的生长和侵袭
Authors Gao J, Zeng K, Liu Y, Gao L, Liu L
Received 15 August 2018
Accepted for publication 10 November 2018
Published 24 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 169—179
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S184078
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Introduction: Melanoma
has been reported as the most common malignancy in skin cancer. The small
nucleolar RNA host gene 5 (SNHG5), an lncRNA, has been proven as a vital
regulator in several types of carcinoma. This study was designed to investigate
the detailed roles and possible mechanisms of SNHG5 in melanoma progression.
Methods: Quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis was conducted to detect the expression levels
of SNHG5, miR-26a-5p and transient receptor potential, canonical 3 (TRPC3 ) mRNA in
melanoma tissues and cells. CCK-8 assay was used to measure the cell viability.
Flow cytometry assays were performed to determine the cell cycle distribution
and apoptosis. The invasive ability was assessed by a 24-well Transwell insert.
Western blot analysis was employed to evaluate the protein expression of TRPC3.
Dual luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, and RNA
pull-down assay were applied to identify the interactions among SNHG5,
miR-26a-5p and TRPC3 .
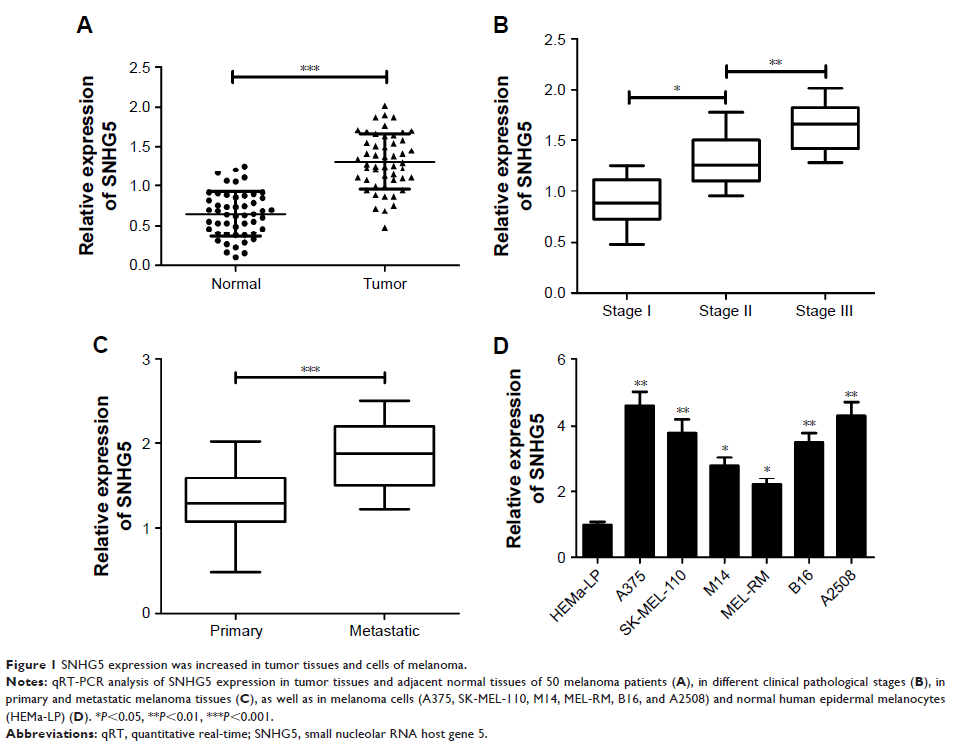
Results: The results
showed that SNHG5 expression was increased in melanoma tumor tissues and cell
lines. Higher SNHG5 expression was correlated with advanced pathogenic status.
Moreover, SNHG5 could serve as a molecular sponge of miR-26a-5p. SNHG5
downregulation repressed proliferation, promoted apoptosis, and decreased
invasion in melanoma cells, while these effects were greatly counteracted by
miR-26a-5p inhibitor. Furthermore, miR-26a-5p directly targeted TRPC3 to
suppress its expression, and this effect was aggravated following SNHG5
downregulation. Also, TRPC3 depletion exerted similar tumor-suppressive
functions as SNHG5 knockdown.
Conclusion: SNHG5
promoted melanoma development by inhibiting miR-26a-5p and facilitating TRPC3
expression, highlighting the potential of SNHG5 as a novel target therapy for
melanoma.
Keywords: lncRNA,
SNHG5, miR-26a-5p, TRPC3, cutaneum carcinoma