110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CUX2 在乳头状甲状腺癌中起着致癌基因的作用
Authors Sun Y, Ye D, Li Y, Chen E, Hao R, Cai Y, Wang Q, Wang O, Zhang X
Received 29 August 2018
Accepted for publication 22 November 2018
Published 24 December 2018 Volume 2019:12 Pages 217—224
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S185710
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: In recent
years, the incidence of thyroid cancer (TC), the most common endocrine
malignancy, has been increasing. Emerging evidence indicates that the
CUT/CUX/CDP family of proteins can play an important role in tumor development
and progression by regulating many cancer-related functions. However, the
molecular functions of CUX2 in TC remain unknown.
Methods: In this
study, we used a series of loss-of-function experiments and Western blot
analysis to investigate the function of CUX2 in TC and the mechanisms involved.
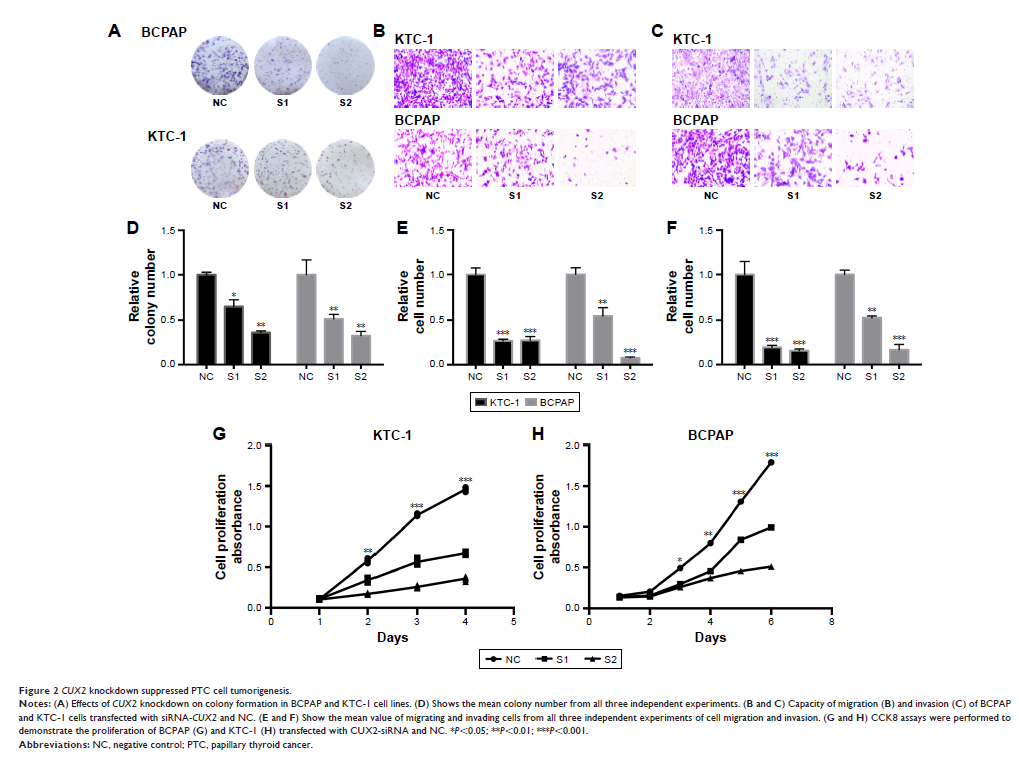
Results: Our data
revealed that CUX2 expression levels were upregulated in
papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Functionally, CUX2 silencing
significantly inhibited PTC cell line (KTC-1 and BCPAP) proliferation, colony
formation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis. Furthermore, CUX2 induced
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and influenced the phosphorylation of
AKT and mTOR in the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathways.
Conclusion: In
summary, CUX2 may
function as a tumor promoter in TC.
Keywords: papillary
thyroid carcinoma, CUX2 , oncogene