110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

食管鳞状细胞癌风险较高地区内镜筛查的诺模图:基于人口的研究结果
Authors Xing J, Min L, Zhang H, Li P, Li W, Lv F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Li H, Guo Q, Wang S, Zhao Y, Wang J, Shi X, Wang A, Zhu S, Ji M, Wu Y, Zhang S
Received 5 March 2018
Accepted for publication 9 July 2018
Published 3 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 431—442
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167311
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Endoscopy
is the main approach used for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
screening, especially in high-risk areas. However, little consensus has been
achieved in recent ESCC screening programs, and endoscopists have selected
patients only by age and family history.
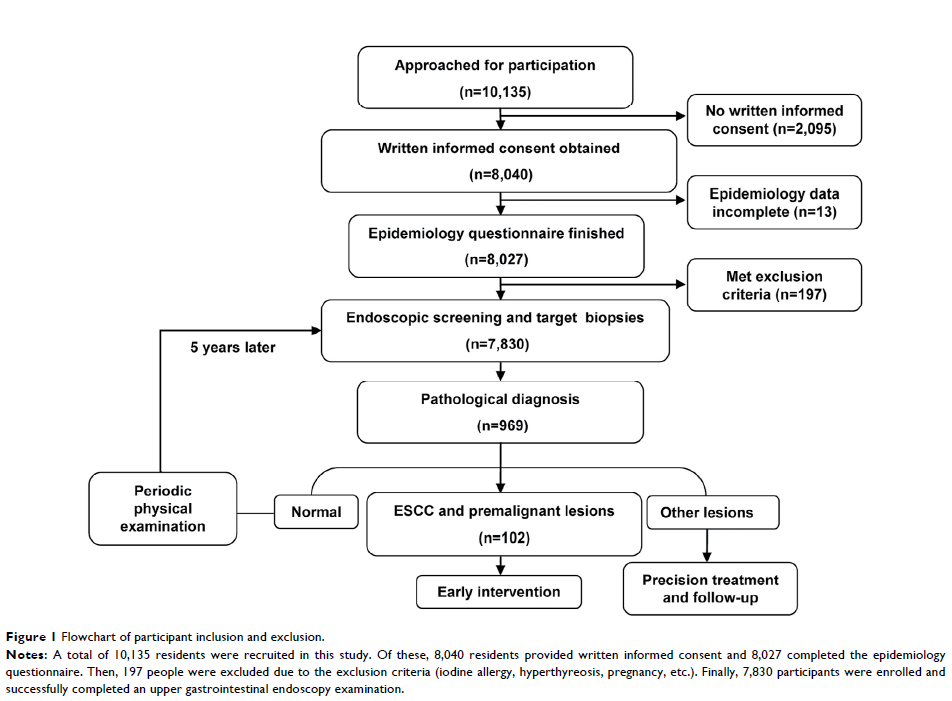
Patients and methods: To
generate a proper strategy for selecting an eligible population for endoscopic
screening based on demographic factors, lifestyle, and eating habits, a total
of 7,830 residents in an area with a high risk of ESCC were recruited for this
study. All participants underwent endoscopic examinations that were conducted
by experienced endoscopists. Risk factors for ESCC and other lesions were
selected by univariate and multivariate logistic regressions. A nomogram for
the prediction of ESCC and premalignant lesions was constructed, which included
information on age, sex, occupation, labor intensity, income, and mining
exposure. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed
to present the predictive accuracy of the nomograms.
Results: The area
under the curve (95% CI) was 0.749 (0.711–0.788) for this nomogram. By applying
this nomogram, we could exclude 60% (4704/7830) of patients before endoscopy
screening and detect all ESCC cases as well as most esophageal lesions in the
remaining population.
Conclusion: In
conclusion, we provided a ready-to-use preclinical tool with the potential to
select eligible people with high risk of ESCC for endoscopy screening.
Keywords: nomogram,
endoscopy screening, ESCC, population-based study