110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对有害结直肠扩张引起的背角神经元伤害性反应施行强度依赖性方式的电针抑制
Authors Yu L, Wang W, Li L, Qin Q, Yu Y, Liu K, Zhao Y, Rong P, Zhu B
Received 6 August 2018
Accepted for publication 9 November 2018
Published 3 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 231—242
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S182876
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr E Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Background: The
transmission of visceral nociception can be inhibited by electroacupuncture
(EA) at the spinal level. However, relationships between current intensity and
EA-induced analgesia are still lacking. This study compares the effects of
different intensities of EA at local acupoints and heterotopic acupoints on
nociceptive responses of spinal wide dynamic range (WDR) neurons induced by
noxious colorectal distension (CRD).
Materials and methods: Experiments
were conducted on 40 Sprague Dawley rats anesthetized with 10% urethane.
Discharges of WDR neurons in the L1–L3 segments of the dorsal horn of the
spinal cord were recorded extracellularly by glass micropipettes. Different
intensities of EA (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 mA, 0.5 ms, 2 Hz) were applied to
contralateral “Zusanli” (ST 36) or “Neiguan” (PC 6), with either the same or
different segmental innervation of the colon.
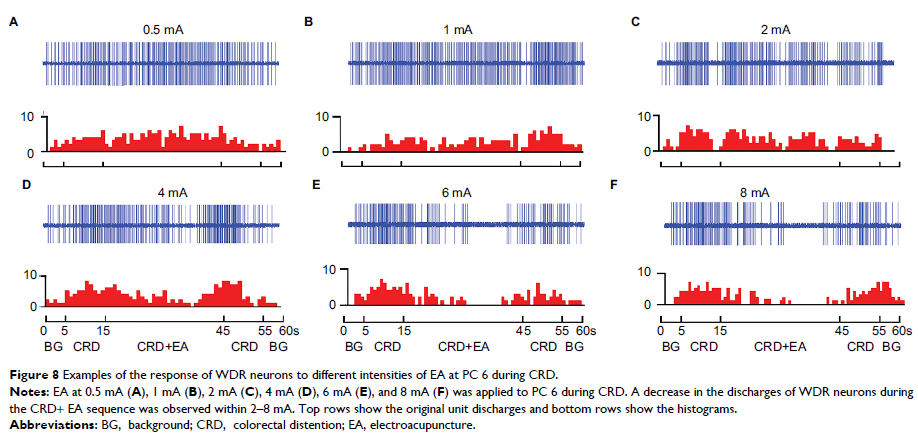
Results: In local
acupoints, the increased discharges of WDR neurons evoked by CRD were
significantly inhibited by EA at 0.5–8 mA. A positive relationship between
current intensity and the inhibiting rate was observed within 0.5–4 mA, but the
inhibiting rate reached a plateau when EA exceeded 4 mA. In heterotopic
acupoints, the increased discharges of WDR neurons evoked by CRD were
significantly inhibited by EA at 2–8 mA. A positive relationship between
current intensity and the inhibiting rate was observed within 2–6 mA. Further
increase in the current beyond 6 mA also resulted in a plateau effect.
Conclusion: Within a certain
range, the nociceptive responses of dorsal horn neurons induced by CRD could be
inhibited by EA in an intensity-dependent manner.
Keywords: electroacupuncture,
current intensity, wide dynamic range, colorectal distension