110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

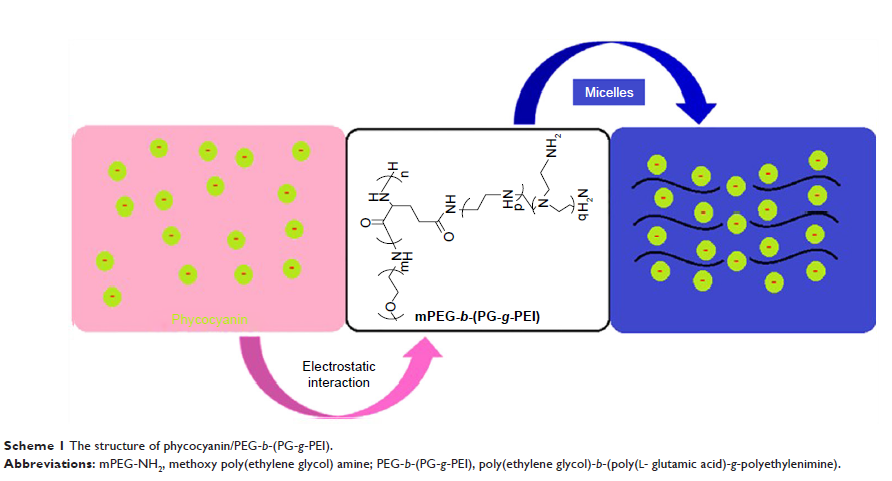
藻蓝蛋白/PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI) 减轻肝脏缺血/再灌注诱导的胰岛损伤及扩大的胰岛功能
Authors Tong F, Tang X, Liu D
Received 15 October 2018
Accepted for publication 10 December 2018
Published 3 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 339—351
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S190938
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion-induced pancreatic islet injury (HI/RIPII) was an
important pathophysiological phenomenon in clinics. In the present study, we
observed the effects of phycocyanin on HI/RIPII. However, the half-life of
phycocyanin was extremely short and limited its use in vivo.
Materials and methods: In order
to overcome this shortcoming, poly(ethylene glycol)-b -(poly(L-glutamic
acid)-g -polyethylenimine)
(PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI)) was
synthesized and estimated as a nanocarrier for lengthening delivery of
phycocyanin through the abdominal subcutaneous injection in rats. Phycocyanin
(isoelectric point=4.3) was encapsulated with PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI) via
electrostatic interactions at pH 7.4.
Results: In vitro
phycocyanin was fast and efficiently encapsulated and showing efficient loading
and sustained release. In vivo the anti-HI/RIPII function of
phycocyanin/PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI) complex was
surveyed in rats using free phycocyanin as the controls, and the results showed
that phycocyanin/PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI) complex reduced HI/RIPII property and enlarged
islet functionality.
Conclusion: These
results suggested that PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI) might be treated as a potential phycocyanin
nanocarrier.
Keywords: phycocyanin,
PEG-b -(PG-g -PEI), HI/RIPII,
pancreatic islets