110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FOXN2 在乳腺癌中得到下调并通过调节 SLUG 来调控迁移、侵袭和上皮 - 间质转化
Authors Ye H, Duan M
Received 12 June 2018
Accepted for publication 3 August 2018
Published 4 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 525—535
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S176938
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Introduction: Forkhead
box (FOX) N2 (FOXN2), a member of FOX protein family, has been reported to play
critical roles in some types of cancers. However, the expression and function
of FOXN2 in breast cancer remain unclear.
Methods: In the
present work, we explored the detailed molecular mechanism of FOXN2 in breast
cancer. We performed RT-qPCR and Western blotting analysis to detect the
expression of FOXN2 in breast cancer. Colony formation assay, CCK-8 assay,
wound healing assay, and Transwell assay were used to determine the effect of
FOXN2 on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer.
Results: Our
results demonstrated that FOXN2 was downregulated in breast cancer tissues and
cell lines. Downregulation of FOXN2 was correlated with tumor size,
pathological grade, and lymph node metastasis. The in vitro experiments
revealed that the ectopic expression of FOXN2 significantly suppressed the
proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of breast cancer cells, and
inhibition of FOXN2 promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of
breast cancer cells. Moreover, inhibition of FOXN2 facilitated
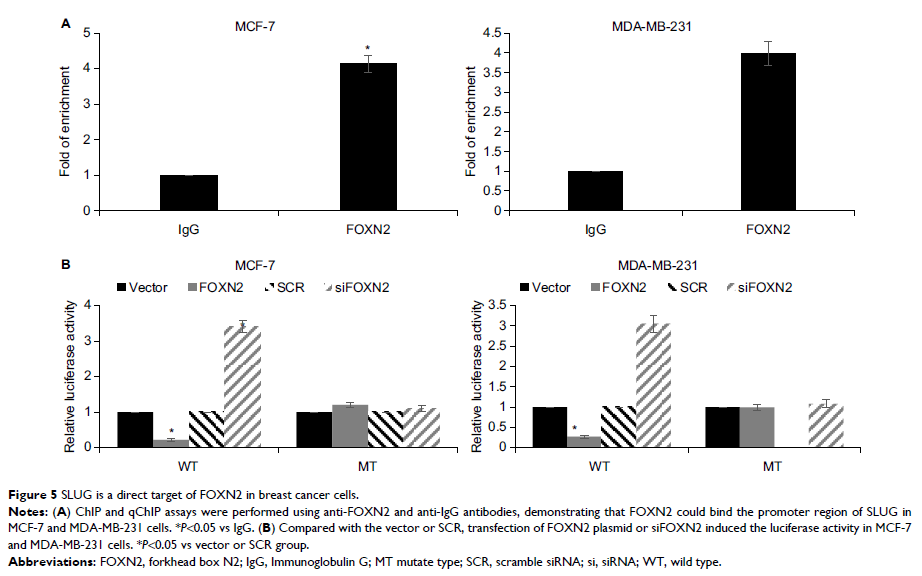
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) through regulation of SLUG.
Conclusion: Taken
together, our results showed for the first time that FOXN2 plays an essential
role in cell proliferation and invasion. Thus, FOXN2 may be an attractive
therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: FOXN2,
proliferation, EMT, SLUG, breast cancer