110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在有或没有既往内窥镜下括约肌切开术的情况下,采用内镜下乳头状大球囊扩张术治疗巨大结石及/或多发性胆总管结石的比较:一个系统评价和荟萃分析
Authors Liu P, Lin H, Chen Y, Wu Y, Tang M, Lai L
Received 4 August 2018
Accepted for publication 7 November 2018
Published 9 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 91—101
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S182615
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Aim: To compare
endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation (EPLBD) alone with EPLBD following
endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) in patients with large and/or multiple common
bile duct stones.
Methods: We
conducted a comprehensive search of PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library
database to identify relevant available articles until July 19, 2018. Complete
common bile duct stone (CBDS) removal rate, frequency of mechanical lithotripsy
(ML) usage, total procedure time and intra- and postoperative adverse events were
analyzed. We used RevMan 5.3 to perform the pooled analyses.
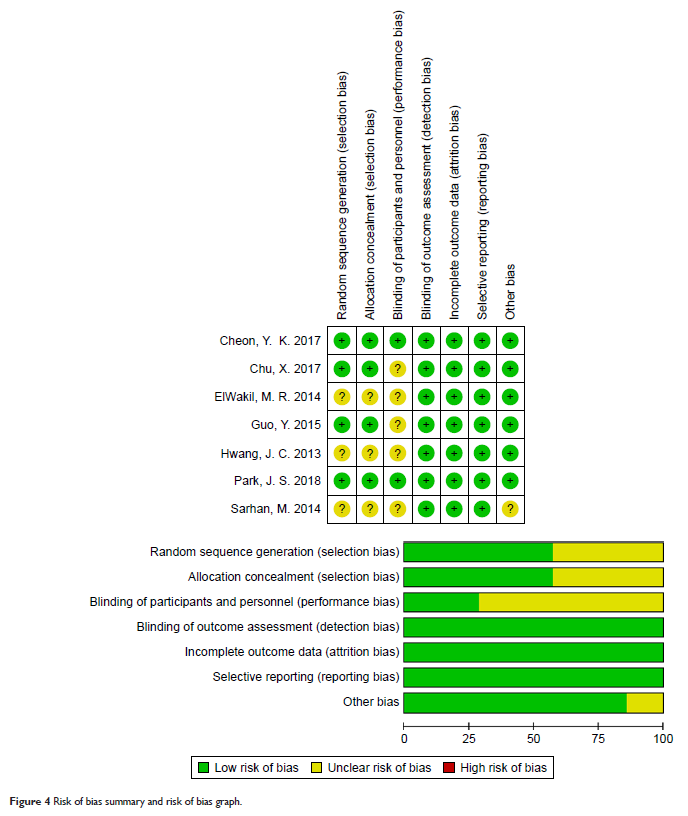
Results: Seven
RCTs matched the selection criteria. A total of 369 patients underwent EPLBD
alone, and 367 patients underwent EPLBD following EST. Our meta-analysis
revealed that there were no significant differences in terms of initial success
rate (OR =0.69, 95% CI=0.44–1.09, P =0.11), frequency of ML usage (OR =1.18, 95%
CI=0.68–2.05, P =0.55),
rate of post-endoscopy pancreatitis (PEP) (OR =0.88, 95% CI=0.43–1.78, P =0.72), total
procedure time (MD =1.52, 95% CI=-0.13–3.17, P =0.07), or other
intra- and postoperative adverse events between the groups for patients with
large and/or multiple CBDSs.
Conclusions: EPLBD
alone was comparable to EPLBD with prior EST in patients with large and/or multiple
CBDSs. Further studies are required to confirm the mechanisms of PEP in
patients who accept EPLBD during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
(ERCP).
Keywords: endoscopic
retrograde holangiopancreatography, ERCP, endoscopic papillary large balloon
dilation, EPLBD, endoscopic sphincterotomy, EST, common bile duct stone, CBDS,
meta-analysis