110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

驱虫药氟苯达唑诱导食管鳞状细胞癌细胞凋亡及抑制 NF-κB 信号通路
Authors Tao J, Zhao H, Xie X, Luo M, Gao Z, Sun H, Huang Z
Received 2 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 December 2018
Published 9 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 471—478
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193206
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background and objectives: The
nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling is activated in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma (ESCC) and can be used as a potential target for anti-ESCC drug
discovery. In this study, we aimed to investigate the function of flubendazole
as a novel NF-κB inhibitor in ESCC cells.
Materials and methods: Cell
Counting Kit-8 assay was carried out to assess cell viability of ESCC cells.
Flow cytometry and immunoblotting were performed to examine cell apoptosis.
Immunoblotting assay was used to analyze the protein expression of NF-κB
signaling. Luciferase assay was performed to explore the activation of NF-κB.
Plasmids were transfected into ESCC cells using Lipofectamine® 2000.
Results: In this
study, the anthelmintic drug flubendazole was found to inhibit the activation
of IκBα kinases (IKKs), block the activation of IκBα, and decrease the
phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, which could be a novel NF-κB inhibitor in ESCC
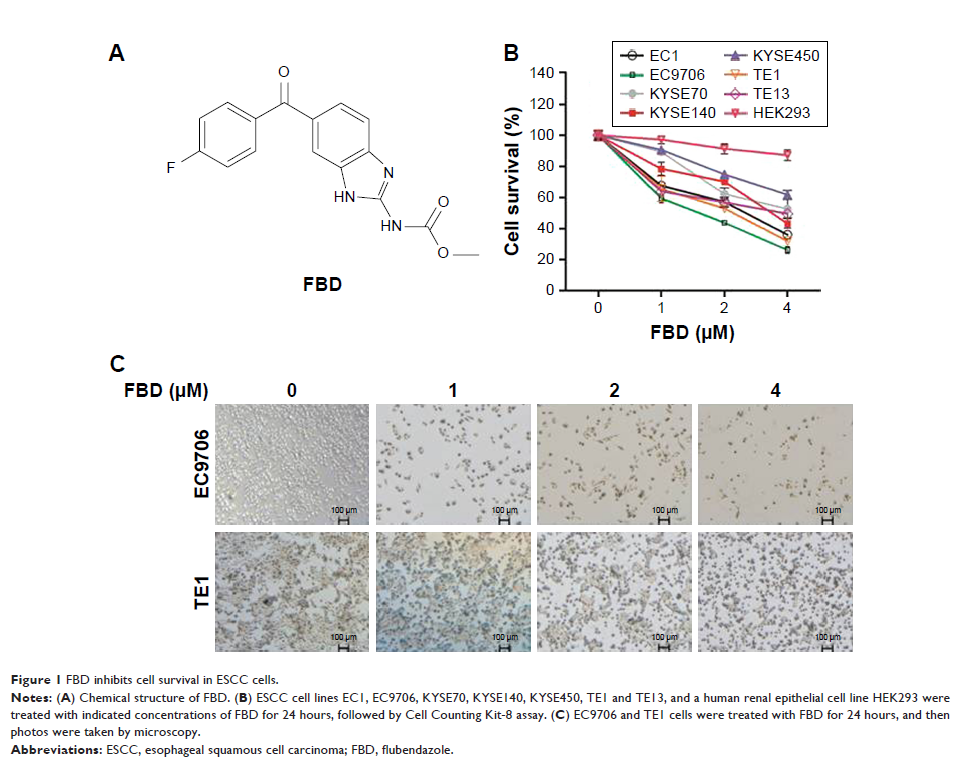
cells. We also found that flubendazole inhibited the cell survival of different
ESCC cells and induced cell apoptosis in both EC9706 and TE1 cells. Moreover,
overexpression of constitutively activated IKKβ markedly decreased the
cytotoxic effect of flubendazole on EC9706 and TE1 cells. In addition,
flubendazole also showed a synergistic effect on ESCC cells when combined with
doxorubicin.
Conclusion: The
results above demonstrated that flubendazole showed its anti-tumor action by
suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and suggested that flubendazole might
be re-purposed for anti-ESCC therapy in clinic as a single agent or in
combination with other anti-tumor drugs.
Keywords: flubendazole,
cell apoptosis, NF-κB, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, re-purpose