110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雷公藤红素通过 TGF-β1/Smad 信号传导抑制结直肠癌
Authors Jiang Z, Cao Q, Dai G, Wang J, Liu C, Lv L, Pan J
Received 17 September 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 9 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 509—518
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187817
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: There are few
clinical challenges associated with the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC).
Studies have shown that TGF-β plays a crucial role in CRC. Importantly,
celastrol, a major components of the root extract of the traditional Chinese
herb Tripterygium
wilfordii Hook F , has been shown to inhibit the growth,
adhesion, and metastasis of human CRC cells through the inhibition of
TGF-β1/Smad signaling.
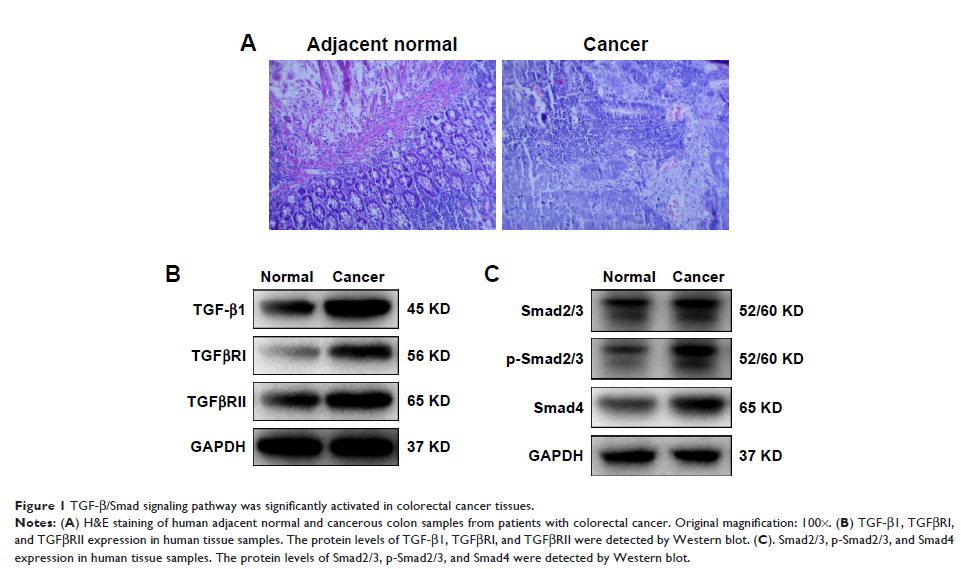
Materials and methods: Real-time PCR
and Western blot tests were proceeded to present TGF-β1, TGF-β receptor type I
(TGFβRI), TGF-β receptor type II (TGFβRII), Smad2/3, p-Smad2/3, Smad4, and
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in human colon cancer cell
samples.
Results: Our results
indicated that celastrol can reduce the expression levels of TGF-β1, TGFβRI,
and TGFβRII in HCT116 and SW620 cells. Furthermore, celastrol could also
prevent the increase in Smad4 and p-Smad2/3 in HCT116 and SW620 cells.
Conclusion: Celastrol could
inhibit tumor growth through TGF-β1/Smad signaling and might be a promising
therapeutic component against CRC.
Keywords: celastrol,
colorectal cancer, TGF-β1, Smad