110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

前列腺癌患者放疗后继发性膀胱癌患病率高:综合分析所产生的证据
Authors Zhao S, Xie Q, Yang R, Wang J, Zhang C, Luo L, Zhu Z, Liu Y, Li E, Zhao Z
Received 30 August 2018
Accepted for publication 13 November 2018
Published 10 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 587—598
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185867
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Objective: To assess
whether radiotherapy (RT) for prostate cancer (PCa) was a risk factor for
secondary bladder cancer (BLCa) through a meta-analysis.
Materials and methods: The MEDLINE,
Embase, and the Cochrane Library were systematically searched for all studies
investigating the risk of BLCa in patients with RT. The association between RT
and risk of BLCa was summarized using hazard ratio with a 95%CI. The protocol
for this meta-analysis is available from PROSPERO (CRD42018090075).
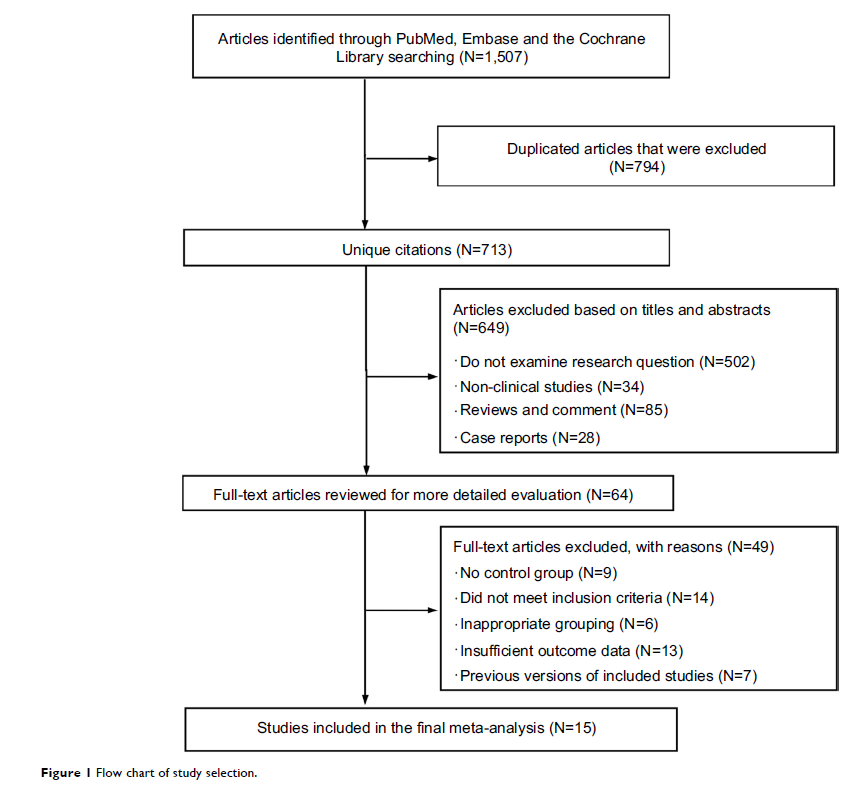
Results: Overall,
619,479 participants (age: 57–79 years) were included from 15 studies, 206,852
of whom were patients who received RT. Synthesis of results indicated that RT
was significantly associated with an increased risk of BLCa compared with the
risk in those who received radical prostatectomy or non-RT (overall HR=1.6,
95%CI: 1.33–1.92, P <0.001). The results were consistent when
restricted to a 5-year lag period (HR=1.84, 95%CI: 1.26–2.69, P =0.002) and
multivariable adjustment (HR=1.96, 95%CI: 1.47–2.62, P <0.001), but
not for 10-year lag period (HR=1.93, 95%CI: 0.9– 4.16, P =0.093) and
brachytherapy subgroup (HR=1.33, 95%CI: 0.87–2.05, P =0.188). The
GRADE-profiler revealed that the rate of events of BLCa on average in the
RT-patients and the non-RT control was 2,462/183,669 (1.3%) and
4,263/382,761(1.1%), respectively; the overall quality of the evidence was low.
Conclusion: Patients
who received RT for PCa was associated with higher risks of developing
secondary BLCa compared to those unexposed to RT, but the absolute effect was
low.
Keywords: prostate
cancer, radiation, radiotherapy, secondary bladder cancer, radical
prostatectomy