110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肽酰基精氨酸脱亚氨酶 4 过表达通过激活 GSK3β/p53 使 MCF-7/ADR 乳腺癌细胞重新对阿霉素敏感
Authors Zhou Q, Song C, Liu X, Qin H, Miao L, Zhang X
Received 18 October 2018
Accepted for publication 10 December 2018
Published 10 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 625—636
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191353
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Adriamycin
(ADR) is widely used in the clinical chemotherapy against breast cancer. But
its efficacy is strongly limited due to the acquisition of multidrug resistance
(MDR). Therefore, acquisition of the resistance to ADR is still a major cause
of chemotherapy failure in breast cancer patients. Peptidylarginine deiminase
IV (PAD4) is reported to target non-histone proteins for citrullination, regulate
their substrate activities, and thereby play critical roles in maintaining cell
phenotype in breast cancer cells. However, whether PAD4 is involved in the
development of MDR in breast cancer is poorly understood.
Materials and methods: We examined the
expression of PAD family members, including PAD4 in ADR-resistant MCF-7 cells
compared with the parental control cells by real-time PCR and Western blotting
analyses. Rescue of PAD4 expression in MCF-7/ADR cells was performed to assess
whether PAD4 could restore the sensitivity of MCF-7/ADR cells to ADR treatment
with cell counting kit-8, flow cytometry, TUNEL, nuclear and cytoplasmic
extract preparations, and immunofluorescence staining analyses.
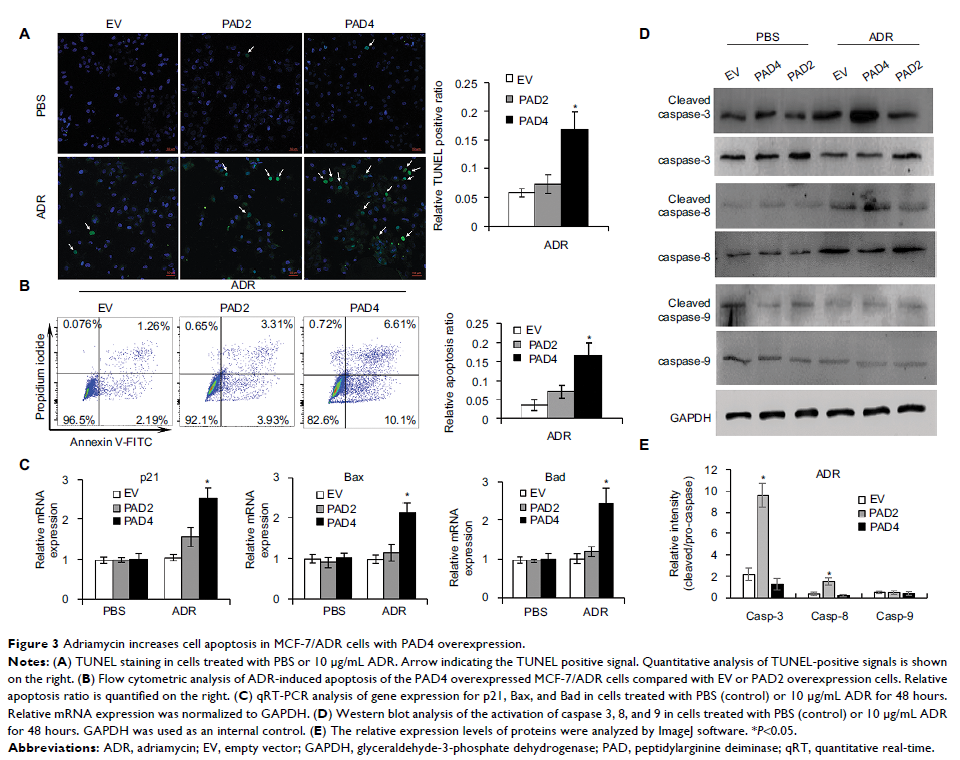
Results: Both PAD2 and
PAD4 were significantly decreased in ADR-resistant cells. However, only PAD4
overexpression can increase the sensitivity of MCF-7/ADR cells to ADR treatment
and decrease MDR1 gene expression. Overexpression of PAD4 in
MCF-7/ADR cells inhibited cell proliferation by inducing cell apoptosis. Under
ADR treatment, overexpression of PAD4 promoted nuclear accumulation of glycogen
synthase kinase-3β and p53, which further activated proapoptotic gene
expression and downregulated MDR1 expression. Moreover, PAD4 activity was
required for activating proapoptotic gene transcripts.
Conclusion: We
demonstrate the previously unappreciated role of PAD4 in reversing ADR
resistance in MCF-7/ADR cells and help establish PAD4 as a candidate biomarker
of prognosis and chemotherapy target for MDR in breast cancers.
Keywords: PAD4,
apoptosis, MDR, breast cancer, GSK3β