110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA SNHG6 通过调节 E2F5 在结直肠癌中的表达而使海绵状 miR-181a-5p 起到竞争性内源性 RNA 的作用
Authors Yu C, Sun J, Leng X, Yang J
Received 5 August 2018
Accepted for publication 12 November 2018
Published 10 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 611—624
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S182719
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Long
noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified as a novel class of regulators
implicated in diverse biological processes in human cancers. Currently,
evidence have shown that SNHG6, a cancer-associated lncRNA, exerts critical
functions in gastric cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma; however, its role in
colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear.
Methods: The
expression of SNHG6 was determined by quantitative real-time PCR in CRC tissues
and cells. SNHG6 was downregulated by using RNAi technology. Cell proliferation
was examined by MTT and clone formation assays. Cell migration and invasion
were determined by wound healing and transwell assays. Fluorescence in situ
hybridization assays were performed to examine subcellular localization of SNHG6
in CRC cells. Fluorescence reporter and Western blot assays were used to
explore the potential mechanisms of SNHG6 in CRC progression.
Results: In this
study, we found that SNHG6 was significantly upregulated in CRC tissues and
cell lines, compared with normal tissues and normal colorectal epithelial cell
line NCM460, respectively. High expression of SNHG6 was positively correlated
with tumor size, advanced TNM stage, and distant metastasis. Survival analyses
revealed that SHNG6 was significantly associated with poor clinical outcomes
and could serve as an independent prognostic factor. Loss-of-function studies
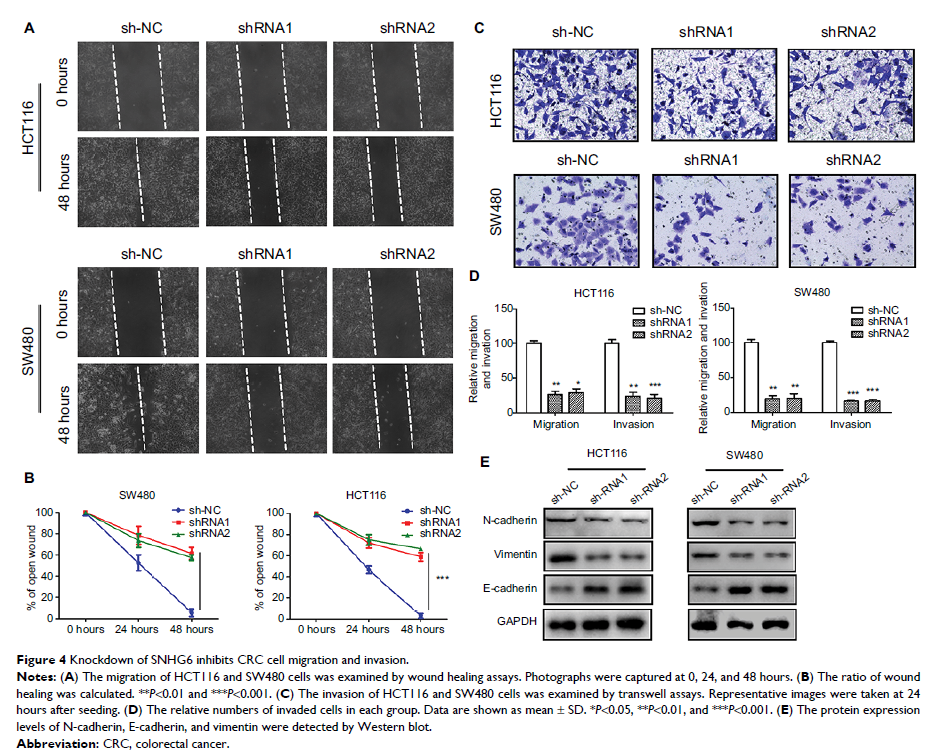
demonstrated that SNHG6 knockdown inhibited CRC cell proliferation, induced
G0/G1 arrest, promoted apoptosis, suppressed CRC cell migration and invasion,
and restrained tumor growth. Mechanistic investigations showed that SNHG6 acted
as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-181a-5p and attenuated the inhibitory
effect of miR-181a-5p on E2F5.
Conclusion: Taken
together, these results demonstrated that SNHG6 plays a crucial role in CRC
progression via miR-181a-5p/E2F5 axis. Therefore, SNHG6 may serve as a
prognostic and therapeutic biomarker in CRC.
Keywords: SNHG6,
colorectal cancer, miR-181a-5p, E2F5, proliferation