110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

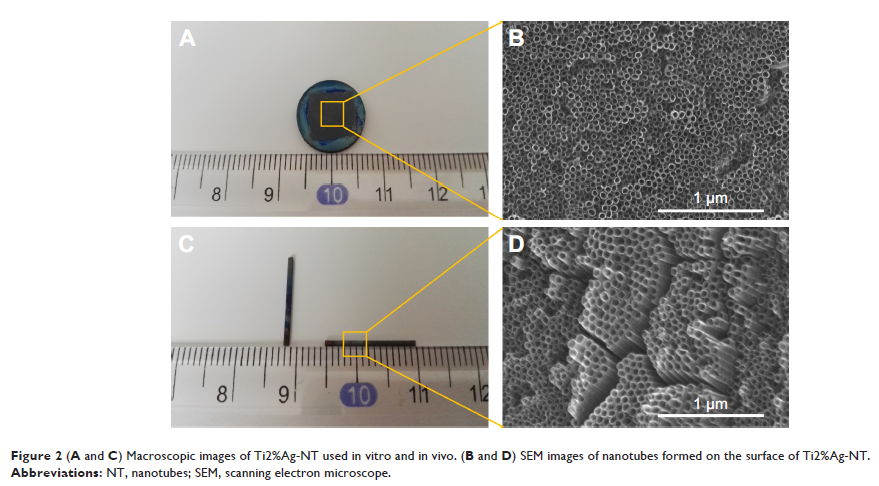
Ti-Ag 合金表面纳米管抗菌薄膜的生物相容性评价
Authors Liu X, Chen C, Zhang H, Tian A, You J, Wu L, Lei Z, Li X, Bai X, Chen S
Received 7 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 December 2018
Published 10 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 457—468
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193569
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Implant-related
infection is a major problem postsurgery. As an alternative to a localized
antibiotic release system, we used Ag to fabricate Ti–Ag alloys with
nanotubular coatings (TiAg-NTs). Ag has excellent antibacterial properties, but
its biological toxicity is a concern. Therefore, we performed biological
experiments both in vitro and in vivo to evaluate the biocompatibility of
TiAg-NTs with different concentrations of Ag (1%, 2%, and 4%).
Methods: For in vitro
experiments, cytocompatibility, including cell attachment, viability, and
proliferation, was tested, and genes and proteins related to osteogenic
differentiation were also evaluated. For in vivo assays, the rat femoral
condylar insertion model was used, and micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and
histological analysis were conducted to analyze bone formation around implants
at 1, 2, and 4 weeks after surgery.
Results: Both in
vitro and in vivo results indicate that Ti2%Ag-NT showed comparable
cytocompatibility with commercially pure Ti (cp-Ti), and it could achieve good
osseointegration with the surrounding bone tissue.
Conclusion: We thus believe
that Ti2%Ag-NT is a potential biomaterial for orthopedics.
Keywords: Ag, Ti, alloy,
nanotube, biocompatibility