110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二甲双胍诱导的凋亡细胞毒性取决于非小细胞肺癌中由 AMPK/PKA/GSK-3β 介导的 c-FLIPL 降解
Authors Luo Z, Zhu T, Luo W, Lv Y, Zhang L, Wang C, Li M, Wu W, Shi S
Received 5 July 2018
Accepted for publication 3 December 2018
Published 11 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 681—689
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S178688
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: Metformin, a
first-line antidiabetic drug, has recently been reported with anticancer
activities in various cancers; however, the underlying mechanisms remain
elusive. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of cellular
FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme (FLICE)-inhibitory protein large (c-FLIPL) in
metformin-induced anticancer activity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
vitro.
Materials and methods: Cell
viability was measured by MTT assay. Quantitative real-time PCR was carried out
to detect the level of mRNA of related genes. The expression of related
proteins was detected by Western blot. siRNA was used to silence the expression
of targeted proteins.
Results: Metformin
significantly suppressed proliferation of both A549 and H460 cells in a
dose-dependent manner. Mechanistic studies suggested that metformin killed
NSCLC cells by inducing apoptotic cell death. Moreover, metformin greatly
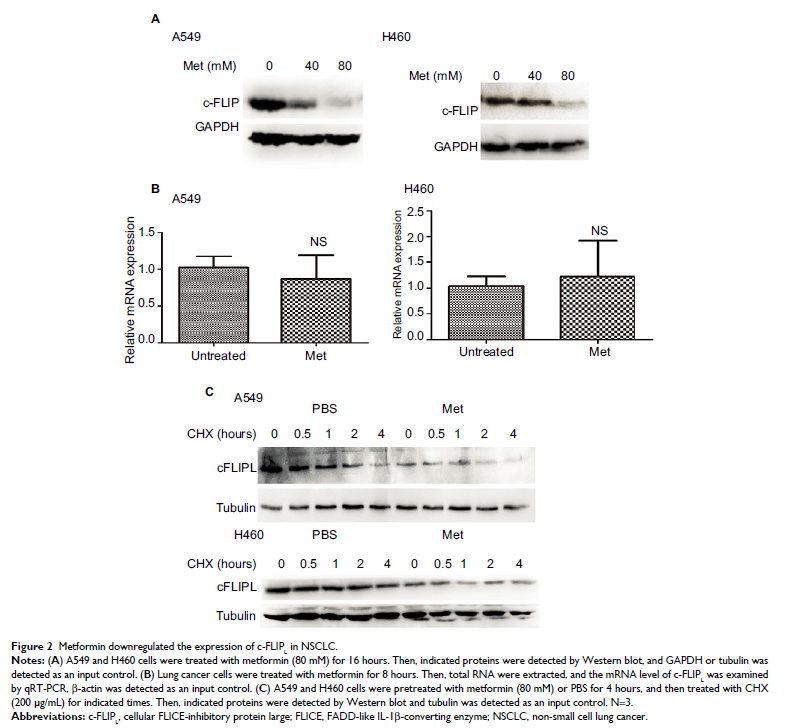
inhibited c-FLIPL expression and then promoted its degradation.
Furthermore, metformin significantly activated Adenosine 5′-monophosphate
(AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its downstream glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta (GSK-3β), block the expression of AMPK, and GSK-3β with siRNA
partially reversed metformin-induced cytotoxicity and restored the expression
of c-FLIPL in lung cancer cells. Metformin also
suppressed the activity of AMPK downstream protein kinase A (PKA), PKA
activators, both 8-Br-cAMP and forskolin, greatly increased c-FLIPL expression
in NSCLC cells.
Conclusion: This
study provided evidence that metformin killed NSCLC cells through
AMPK/PKA/GSK-3β axis-mediated c-FLIPL degradation.
Keywords: non-small
cell lung cancer, c-FLIPL, AMPK, GSK-3β, PKA