110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于莱鲍迪甙 A 的新型自纳米胶束化固体分散系统:用于口服递送姜黄素的潜在纳米平台
Authors Hou Y, Wang H, Zhang F, Sun F, Xin M, Li M, Li J, Wu X
Received 18 October 2018
Accepted for publication 30 November 2018
Published 11 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 557—571
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S191337
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: Rebaudioside A
(RA) has nanocarrier characteristics that allow it to self-assemble into
micelles in aqueous solutions. The purpose of this study was to determine if a
self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion based on RA could be utilized as an oral
nano-drug delivery system.
Materials and methods: Curcumin
(Cur) served as a model hydrophobic drug, and a Cur-loaded self-nanomicellizing
solid dispersion based on RA (RA-Cur) was formulated. The properties of RA-Cur
in the solid state and in aqueous solution were characterized. The antioxidant
activity and mechanism of RA-Cur endocytosis were also investigated. The
pharmacokinetics, biodistribution in the intestinal tract, and
anti-inflammation properties were also evaluated in vivo.
Results: RA-Cur
could be easily fabricated, and it self-assembled into ultrasmall micelles
(particle size ~4 nm) in a homogeneous distribution state (polydispersity
index <0.2) when dissolved in water. Cur was readily encapsulated into
RA micelles and this improved its water solubility (to 14.34±1.66 mg/mL), as
well as its in vitro release and membrane permeability. The antioxidant
activities of Cur in RA-Cur were also significantly improved. Biodistribution
in the intestinal tract confirmed a significant enhancement of Cur absorption
in the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum by encapsulation in RA-Cur, and the
absorption of RA-Cur was governed by mixed transcytosis mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetic tests of RA-Cur in rats revealed a dramatic 19.06-fold
enhancement of oral bioavailability when compared to free Cur. More
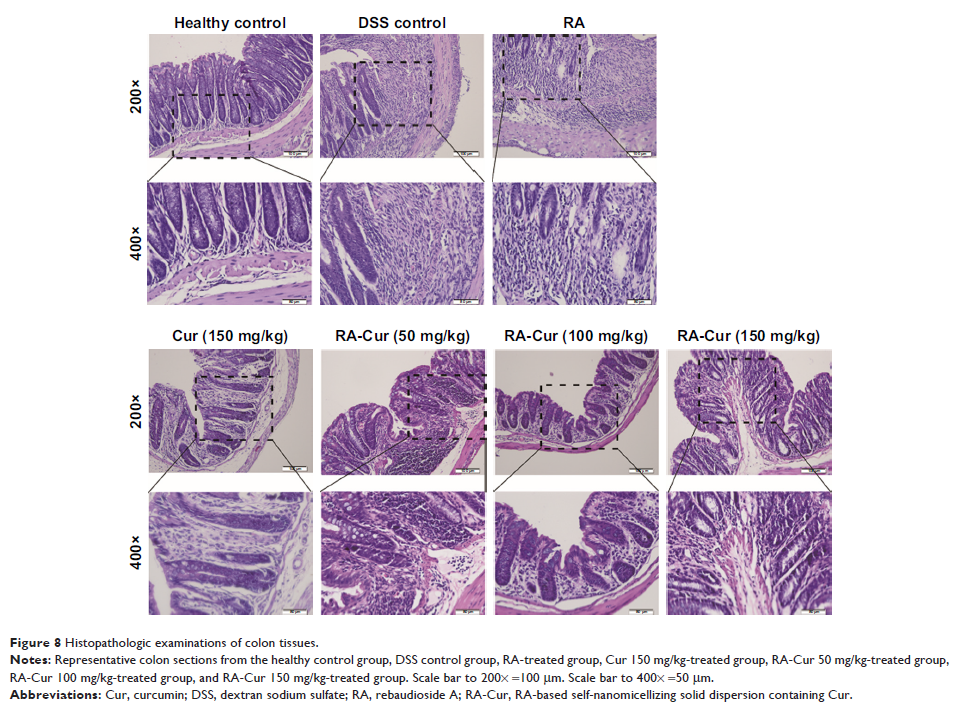
importantly, oral administration of RA-Cur could efficiently ameliorate
ulcerative colitis in a mouse model induced by dextran sodium sulfate.
Conclusion: Self-nanomicellizing
solid dispersions based on RA have great potential as novel oral nano-drug
delivery systems for hydrophobic drugs such as Cur.
Keywords: rebaudioside
A, curcumin, self-nanomicellizing, micelle, solid dispersion, drug delivery